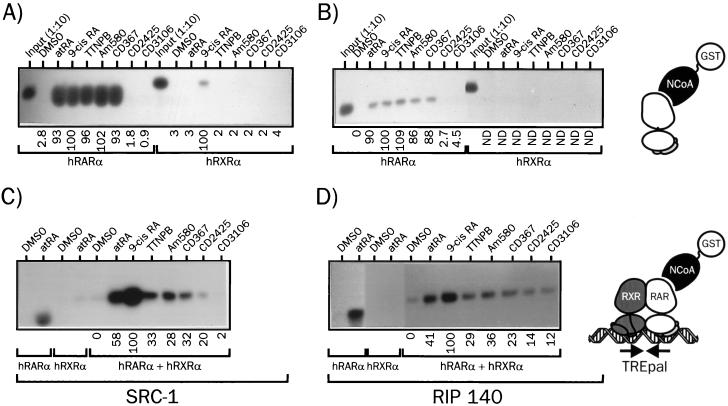
FIG. 2.
Assembly of hRARα into a DNA-bound heterodimer induces ligand-selective recruitment of SRC-1 and RIP140. (A) Interaction of hRARα or hRXRα with SRC-1 in the presence of various retinoids. 35S-labeled hRARα or hRXRα was incubated with the indicated activating ligand (10 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 2 h and then with the fusion protein GST-SRC1(382–842). Complexes were precipitated with glutathione-Sepharose beads and extensively washed. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (8% gel), and receptors were detected by autoradiography. (B) Interaction of hRARα or hRXRα with RIP140. Receptors were synthesized in vitro as described in the text and incubated in the presence of retinoids and a GST-RIP140(752–1158) fusion protein. Following washing, proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and revealed by autoradiography. In input lanes, 1/10 of the input from in vitro-coupled transcription-translation mix was analyzed in parallel. (C) Interaction of DNA-bound hRXRα-hRARα heterodimers with SRC-1. 35S-labeled hRXRα, hRARα, and the DNA probe TREpal were incubated as described in Materials and Methods to ensure >95% heterodimer formation. These complexes were then incubated in the presence of the activating ligand for 2 h (10 μM) and then with the GST–SRC-1 fusion protein for an additional 2 h. Complexes were precipitated and analyzed as described above. (D) Interaction of DNA-bound hRXRα-hRARα heterodimers with RIP140. The procedure was similar to that described for panel C except that SRC-1 was substituted for RIP140. The TREpal sequence is cggtagAGGTCATGACCTctcg. Numbers below gel lanes indicate the amount of radiolabeled receptor bound to SRC-1 or RIP140 in the presence of the indicated ligand relative to that measured in the presence of 9-cis RA, defined as 100%. Values represent mean data from four independent experiments carried out with two different bacterial extracts. ND, not determined. Standard errors never exceeded 5.3%. Representative autoradiograms are shown.