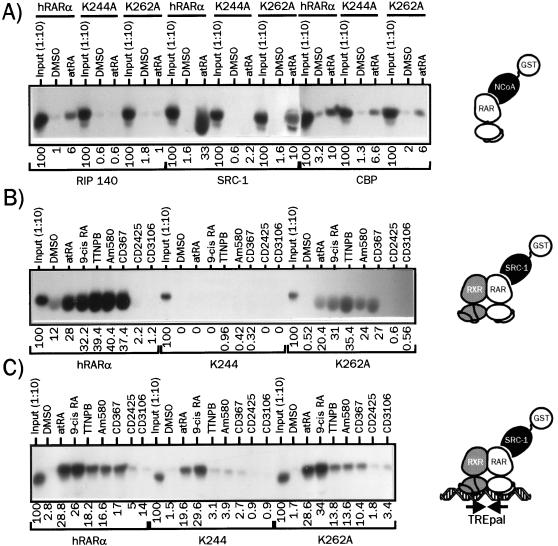
FIG. 6.
Lysine 244 and lysine 262 are differentially involved in NCoA binding by liganded hRARα. (A) Interaction of monomeric hRARα and of K244A and K262A derivatives with RIP140, SRC-1, and CBP(1-1099). GST fusion proteins corresponding to the indicated coactivator were incubated in the presence of 35S-labeled, atRA-bound receptors. Complexes were isolated by adsorption on a glutathione-linked agarose beads and analyzed by SDS-PAGE (8% gel) as described for Fig. 1. (B) Interaction of monomeric wt and receptor mutants with SRC-1 in the presence of natural and synthetic retinoids. 35S-labeled hRARα derivatives were incubated with or without 10 μM ligand, and SRC-1-associated receptors were isolated and analyzed as described above. (C) Mutation of K244 disrupts synthetic retinoid-induced SRC-1 recruitment by DNA-bound heterodimers. The ability of each hRARα derivative to bind to SRC-1 when incorporated into a TREpal-bound heterodimer was assessed as described for Fig. 1 in the presence of the indicated ligand. In the control lanes, 1/10 of the coupled transcription-translation mix used to produce radioinert hRARα was used to assess the efficiency of synthesis by label incorporation. Products were analyzed in parallel with other samples containing labeled hRXRα. Numbers below gel lanes indicate the amount of radiolabeled receptor bound to the indicated coactivator RID in the presence of the indicated ligand relative to total labeled receptor input, defined as 100%. Values represent mean data from four independent experiments carried out with two different bacterial extracts. Standard errors never exceeded 7.2%. Representative autoradiograms are shown.