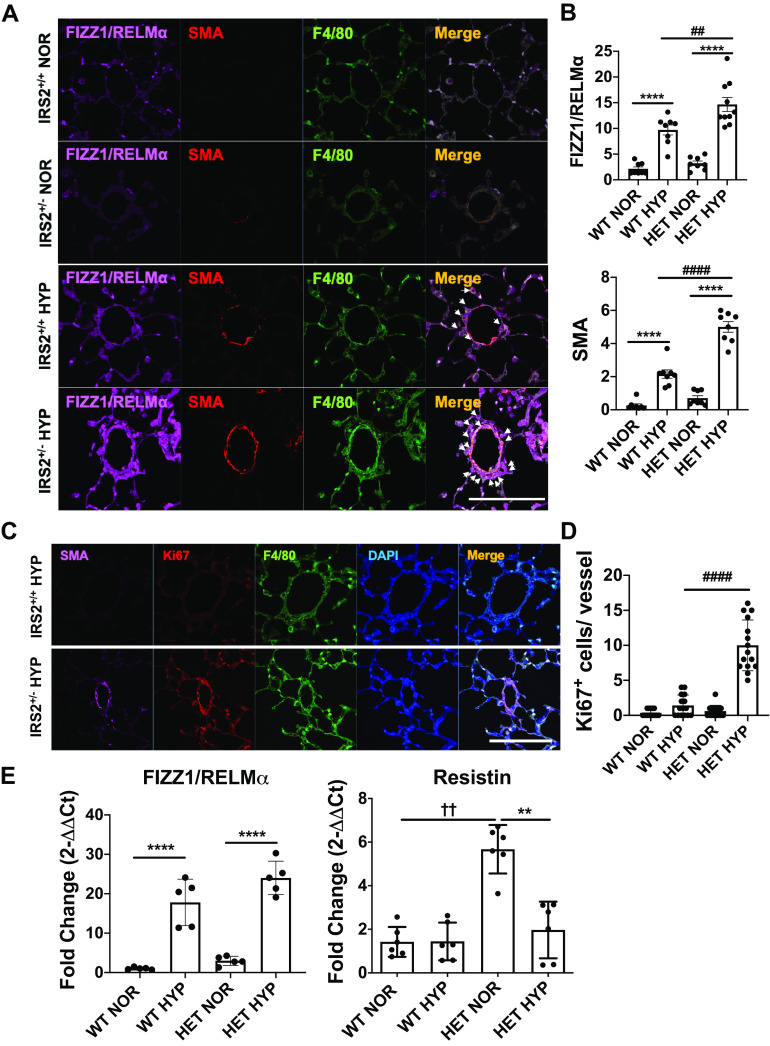
Figure 3.
Perivascular FIZZ1/RELMα expression, cell proliferation, and muscularization are exacerbated in the lungs of IRS2+/− mice by 4 days of hypoxia. A: macrophage recruitment and muscularization in IRS2+/+ and IRS2+/− mice in response to 4 days of hypoxia (10% O2). Colocalization of perivascular muscularized cells (SMA+, red), macrophages (F4/80+, green), and RELMα (marker for M2 macrophages, far red) is indicated by arrows. B. quantification of FIZZ1/RELMα and SMA expression in the pulmonary vessels. Fluorescence intensity data are expressed as means ± SD. ##P < 0.01, ####P < 0.0001, ****P < 0.0001 versus indicated group (n = 5–6 animals). Scale bars = 100 µm. C: representative images show perivascular muscularization (SMA+, far red), cell proliferation (Ki67+, red), and macrophages (F4/80+, green) in the pulmonary vasculature of hypoxia-stimulated IRS2+/+ (top) and IRS2+/- (bottom) mice. D: hypoxia induced significantly more vascular cell proliferation in IRS2+/− mice than in IRS2+/+ mice. Data are expressed as means ± SD. ####P < 0.001 (n = 15 vessels). E: hypoxia induction of Retnla gene expression in whole lung tissue from IRS2+/+ and IRS2+/− mice. Data are expressed as means ± SD. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001, ††P < 0.001 versus indicated group (n = 5–6 animals). IRS2, insulin receptor substrate 2; HYP, hypoxia; NOR, normoxia; RELMα, resistin-like molecule α.