Figure 1. Schematic of Phos-tag immunoblot analysis.
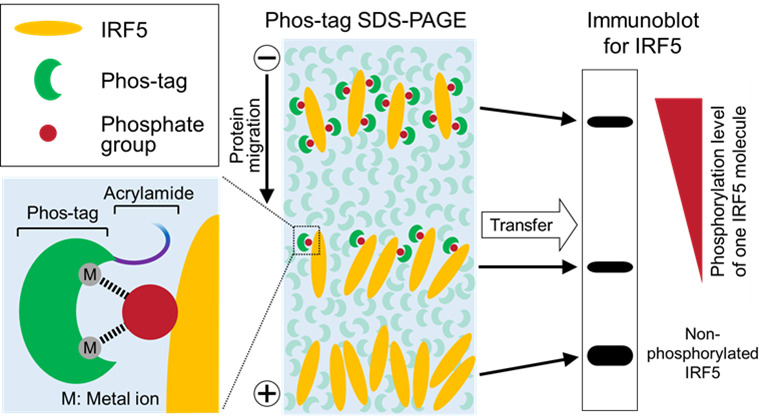
Phos-tag binds specifically to a phosphate group on the target protein via metal ions, such as Zn2+ or Mn2+. Non-phosphorylated and phosphorylated forms of the target protein (IRF5 in this figure) are separated by SDS-PAGE using acrylamide conjugated with Phos-tag, and then detected by immunoblot analysis using an appropriate specific antibody. The mobility shift of the phosphorylated protein is caused by trapping of its phosphate groups by the polyacrylamide gel-conjugated Phos-tag. Thus, multiple phosphorylations of IRF5 appear as different up-shifted bands, whose mobility shift increases with the phosphorylation level of each IRF5 molecule.
