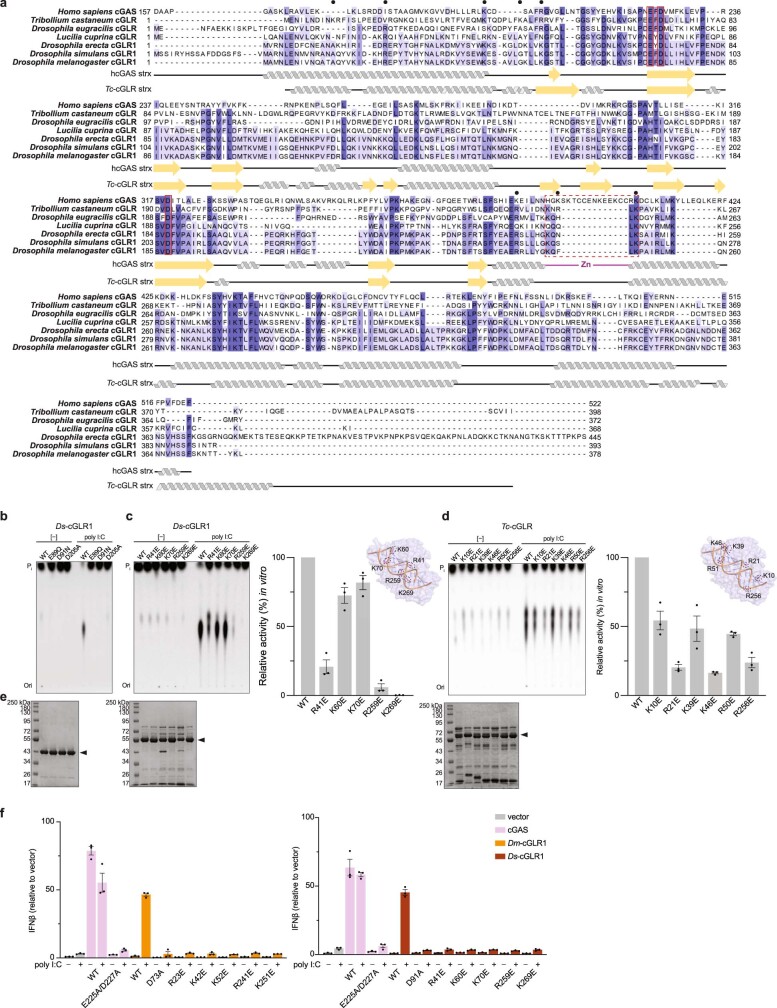
Extended Data Fig. 3. Sequence analysis and mutagenesis of insect cGLRs.
a, Alignment of the catalytic domain of hcGAS and active cGLRs identified in T. castaneum, D. eugracilis, L. cuprina, D. erecta, D. simulans and D. melanogaster. The EhD[X50–90]D catalytic triad is highlighted with a red outline and the human Zn-ribbon insertion that is absent in insect cGLRs is denoted with a red dashed outline. Predicted basic ligand-binding residues selected for mutational analysis denoted by black circles. cGLRs from D. erecta and D. simulans are close homologues of Dm-cGLR1 (76% and 91% sequence identity, respectively) and thus are also referred to as ‘cGLR1’. All biochemical experiments with Ds-cGLR1 were performed with a construct beginning at M19. b, In vitro reactions demonstrating that mutation of the catalytic residues ablates nucleotide product synthesis by Ds-cGLR1 in response to poly I:C. c, d, In vitro reactions analysing dsRNA recognition through the putative ligand-binding surface by Ds-cGLR1 (c) or Tc-cGLR (d). The insets for panels c and d show models of the Tc-cGLR–dsRNA complex based on the hcGAS–dsDNA structure (PDB: 6CTA)14, indicating predicted dsRNA-interacting residues in Ds-cGLR1 (c) or Tc-cGLR (d). Charge swap mutation to these residues variably disrupted poly I:C-stimulated activity by Ds-cGLR1 and Tc-cGLR, shown by TLC (left) and quantified relative to WT activity (right). Data in b–d are representative of n = 3 independent experiments. e, SDS–PAGE and Coomassie stain analysis of purified WT and mutant proteins, as labelled in the above TLC images. f, IFNβ luciferase assay in which cGLRs are expressed in human cells and CDN synthesis is detected by mammalian STING activation, as in Fig. 2e. IFNβ was quantified relative to the empty vector control. In comparison to hcGAS control, which is activated by expression vector-plasmid DNA, Dm-cGLR1 (left) and Ds-cGLR1 (right) strictly require poly I:C stimulation to activate a downstream STING response. Mutation to catalytic residues or putative ligand-binding residues ablates cGLR1 signalling. See Fig. 2e: Dm-cGLR1 activity quantified relative to WT activity upon poly I:C stimulation. Data are mean ± s.e.m. of n = 3 technical replicates and representative of n = 3 independent experiments.