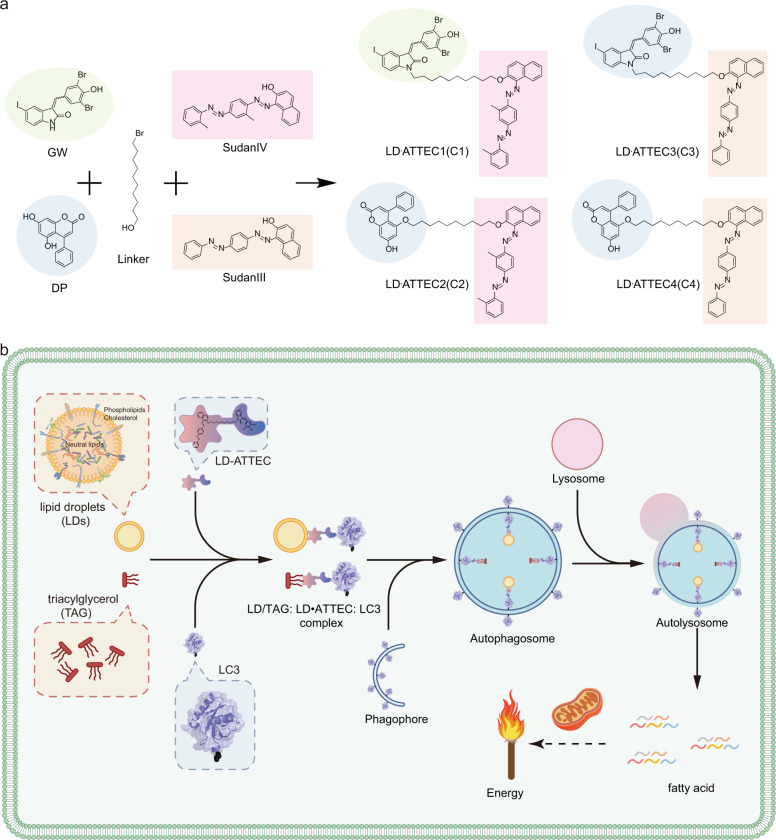
Fig. 1. Compound structures and designing/working principle.
a The simplified synthesis diagram of LD·ATTECs (C1–C4) utilized in this study. b A schematic illustration of the mechanism of action of LD·ATTEC-mediated lipid degradation. LD·ATTECs bind to LDs or neutral lipids (using TAG as a typical example) via hydrophobic interactions and the autophagosome protein LC3 simultaneously, leading to formation of the LD/TAG–LD·ATTEC–LC3 ternary complex, engulfment of the complex into autophagosomes, and subsequent autophagic degradation of LD/neutral lipids after autophagosome–lysosome fusion, providing energy source for the cells through mitochondria.