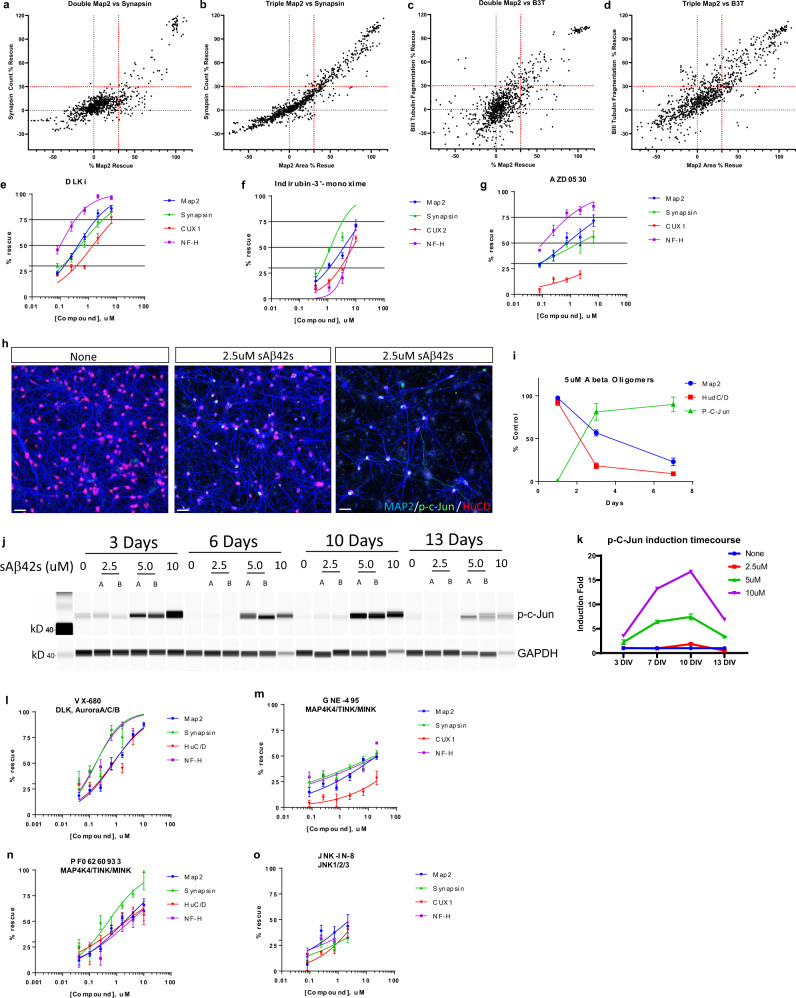
Fig. 5. Focused small-molecule screen identifies DLK-JNK-cJun pathway inhibition protects human neurons from Aβ oligomer toxicity.
a–d Neurons and astrocytes (a, c) or neurons, astrocytes, and microglia (b, d) were treated with 5 μM sAβ42s and small molecules from a focused screen of known neuroprotective agents at multiple concentrations (50, 25, 12.5, and 6.25 μM (double culture), 50, 12.5, 3.1, and 0.78 μM (triple culture). Results were graphed as Synapse % rescue versus MAP2 % rescue (a, b) and Beta III tubulin % rescue versus MAP2 % rescue (c, d). Small molecules that prevented toxicity in dendrites (MAP2), synapses (Synapsin 1/2), cell count (CUX2), or axons (NFL-H) at or above 30% were considered hits (red dotted line); anti-Aβ antibody used as a positive control that prevented all types of toxicity. e–g Further validation of top hits DLKi (e), Indirubin-3′-monoxime (f), and AZD0530 (g) from the focused screen by IC50 curves against MAP2 (blue), Synapsin 1/2 (green), CUX2 (red), and NFL-H (purple). h sAβ42s treatment induced expression of p-cJun (green) in the nucleus (HuCD, red). i Quantification of MAP2 (blue), HuC/D (red), p-cJun (green) staining indicated an increase in cJun phosphorylation with prolonged sAβ42s treatment. j 22-week-old iPSC neuron culture treated with sAβ42s showed dose-dependent, sustained phosphorylation of cJun as shown by western blot. GAPDH served as the loading control. k Western blot quantification of p-cJun induction normalized to GAPDH. l–o Inhibition of known components of DLK-JNK-cJun pathway using small molecules VX-680 (l), GNE-495 (m), PF06260933 (n), JNK-IN-8 (o) prevents sAβ42s-induced neural toxicity in all measured markers in a dose-dependent manner. Data are presented as mean values +/− SEM and n = 4 wells (e–g, I, k–o). IC50 curves fitted by Prism software (e–g, m–o).