Figure 4.
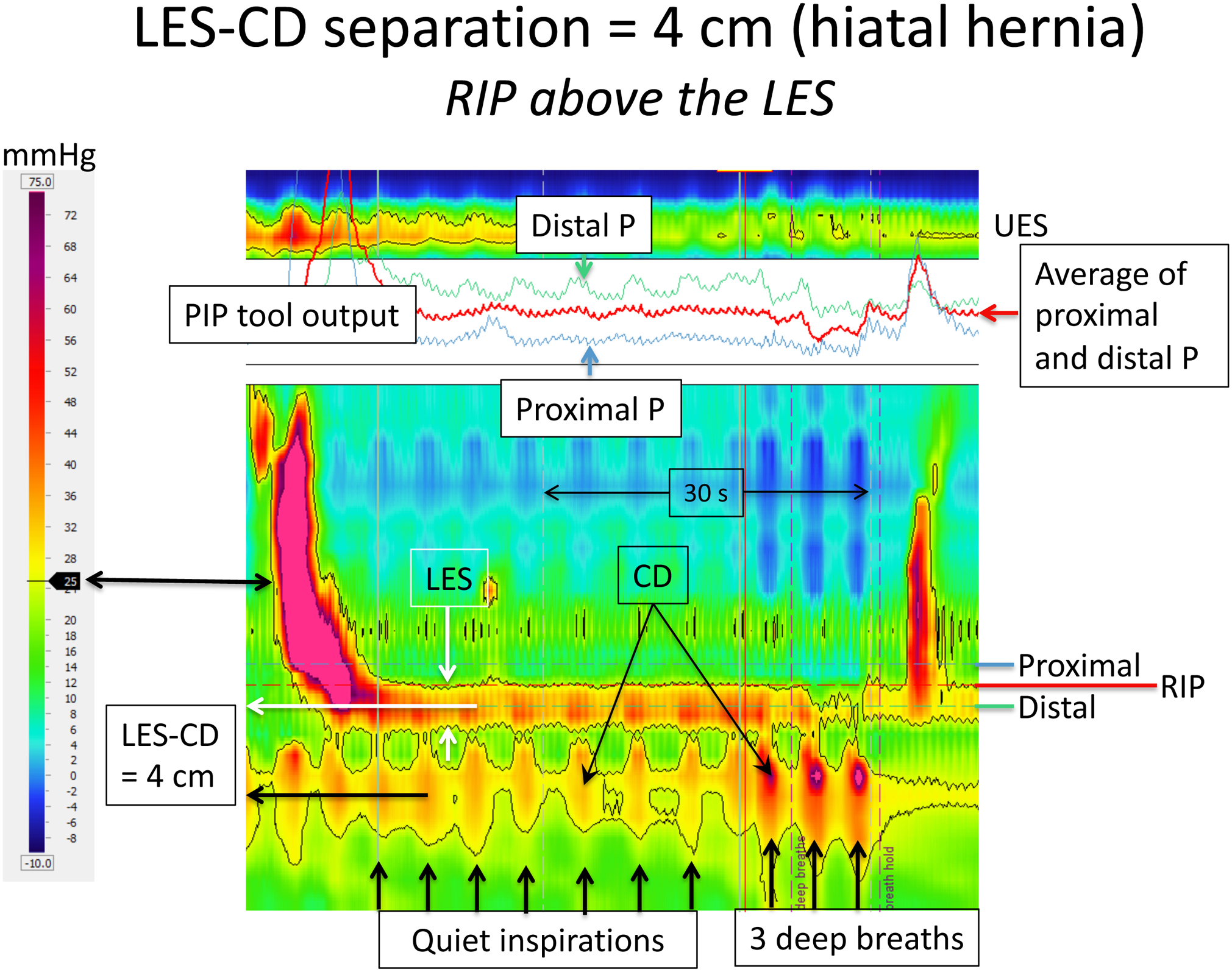
HRM recording of EGJ pressure in an individual with a moderate sized hiatal hernia as evident by the CD being isolated from the LES pressure signature; the LES-CD separation is 4 cm. Formatting of the figure is identical to that of Figures 2 and 3 with the dominant EGJ pressure profile highlighted by the black 25 mmHg isobaric contour and the PIP tool optimally positioned to isolate the RIP. However, in this example, the RIP no longer localizes the CD signal, instead localizing at the proximal margin of the LES. Even without the aid of the PIP tool, that is evident by the inspiratory bursts of red on the LES recording. In fact, the respiratory increases in pressure appear to extend into the distal esophagus in this example (evident by the three deep breaths) emphasizing how the RIP can be unreliable with greater degrees of LES-CD separation. Figure used with permission from the Esophageal Center at Northwestern.
