FIG 5.
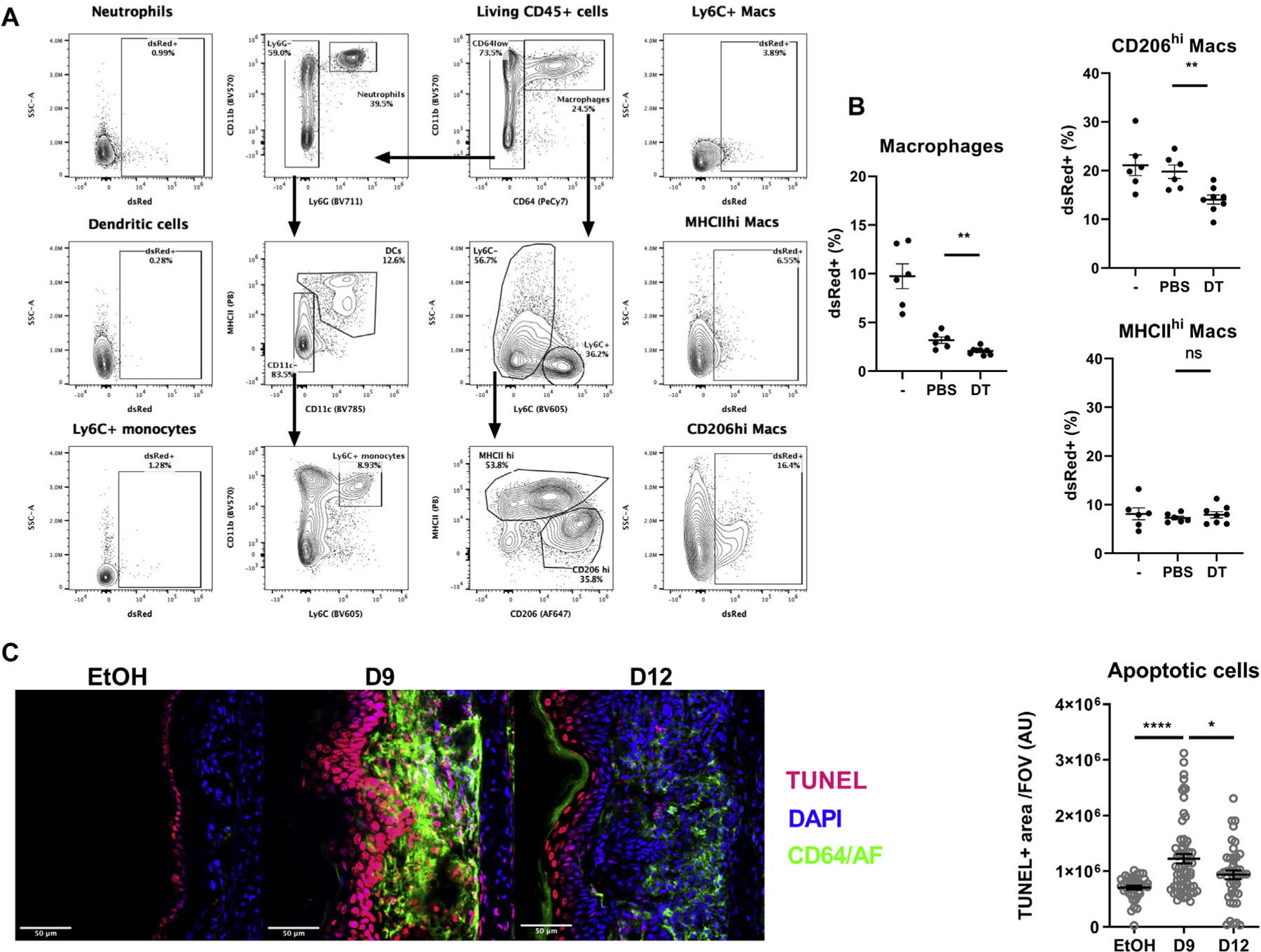
Basophils control dermal-resident macrophage (Mac) efferocytosis. B8×iDTR mice were treated with EtOH (–) or MC903 for 4 days. The MC903-treated mice were depleted of basophils by injections of diphtheria toxin (DT) or PBS. At day (D) 9 after MC903 treatment, 2M dsRed-postive apoptotic cells were injected in the ear dermis. Two hours later the mice were humanely killed and their ear cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. A, Representative gating strategy of skin phagocytes and their uptake of dsRed-positive apoptotic cells. B, Histograms representing the efferocytosis of macrophages and relevant subsets as in (A) (n = 6–8). C, EtOH- or MC903-treated ears were analyzed by immunofluorescence for macrophages and apoptotic cell content was analyzed by TUNEL assay (scale bar = 50 μm). The TUNEL+ area was quantified (n = 5–7 mice with 10 fields of view per mouse). Results are representative of (A and B) or pooled from (C) 2 independent experiments showing similar results. Means ± SEMs are represented. Statistics were calculated by using the unpaired t tests. *P < .05; **P <.01; ****P < .0001. AF, Autofluorescence ns, nonsignificant.
