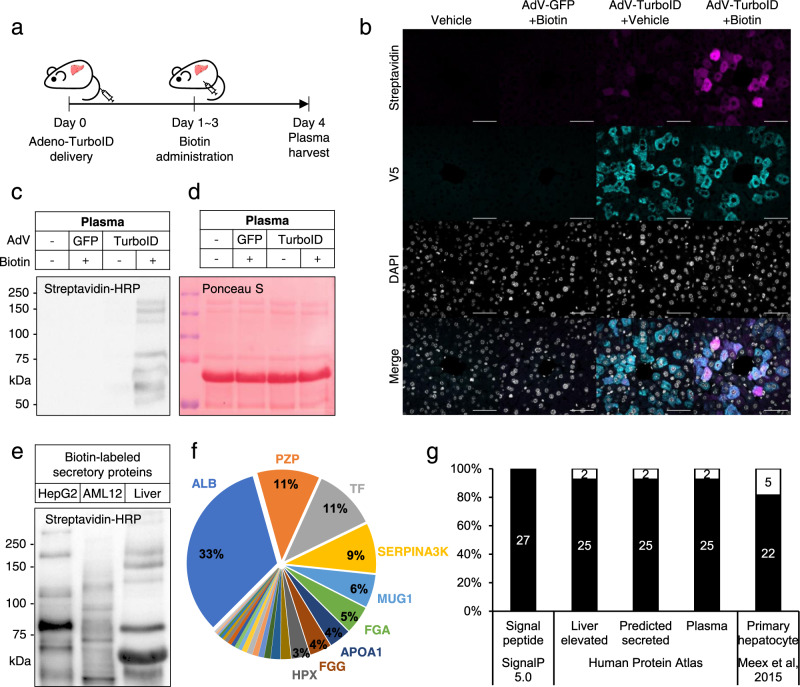
Fig. 3. Identification of liver-specific secretory proteins in plasma from liver iSLET mice.
a Experimental scheme for adenoviral expression of Sec61b-V5-TurboID and biotin labeling in mouse liver tissue. b Immunofluorescence imaging of TurboID (Anti-V5) and biotinylated proteins (Streptavidin-Alexa) in liver tissue sections from GFP or Sec61b-V5-TurboID adenovirus (AdV) transduced mice. Scale bars, 50 μm. These experiments were repeated as biological triplicates with similar results. c, d Streptavidin-HRP detection of biotinylated proteins (c) and Ponceau S staining of proteins (d) in blood plasma from GFP or Sec61b-V5-TurboID adenovirus (AdV) transduced mice. These experiments were repeated as biological triplicates with similar results. e Biotinylated secretory protein profiles generated by Sec61b-V5-TurboID adenovirus in supernatants of hepatocyte cell lines, HepG2 and AML12, and plasma of liver iSLET mice. These experiments were repeated as biological triplicates with similar results. f Relative abundance of biotinylated secretory proteins detected in the plasma of liver iSLET mice in terms of biotinylated spectral counts. ALB, Serum albumin; PZP, Pregnancy zone protein; TF, Serotransferrin; SERPINA3K, Serine protease inhibitor A3k; MUG1, Murinoglobulin-1; FGA, Fibrinogen alpha chain; APOA1, Apolipoprotein A-I; FGG, Fibrinogen gamma chain; HPX, Hemopexin. g Specificity analysis for biotinylated proteins with SignalP 5.0, Human Protein Atlas (HPA), and literature.