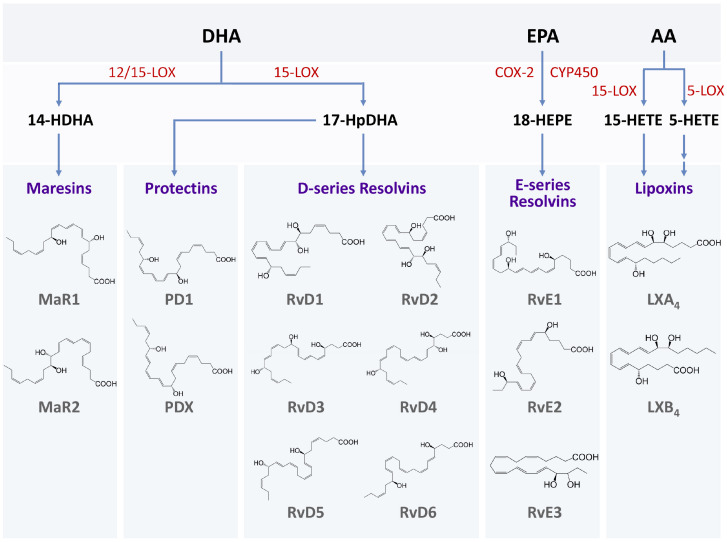
Fig. 1.
SPMs and their biosynthesis. Biosynthesis of SPMs starts from the long-chain PUFAs such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and arachidonic acid (AA). Enzymes, including lipoxygenase (LOX) and cyclooxygenase (COX), convert PUFAs towards various SPM families. Maresins (MaR1 and MaR2), protectins (PD1 and PDX), and D-series resolvins (RvD1-RvD6) are derived from DHA. 14-Hydroxy docosahexaenoic acid (14-HDHA) is the intermediate of maresins produced by 12/15-LOX, and 17-hydroperoxy docosahexaenoic acid (17-HpDHA) is the intermediate of other SPM families derived from DHA. E-series resolvins (RvE1, RvE2, and RvE3) are synthesized from EPA. 18-Hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acid (18-HEPE) is the major intermediate which is produced by COX-2 or CYP450. Lipoxins (LXA4 and LXB4), the first SPMs identified, are biosynthesized from AA in two different routes by either 15-LOX or 5-LOX in different cells or tissues.