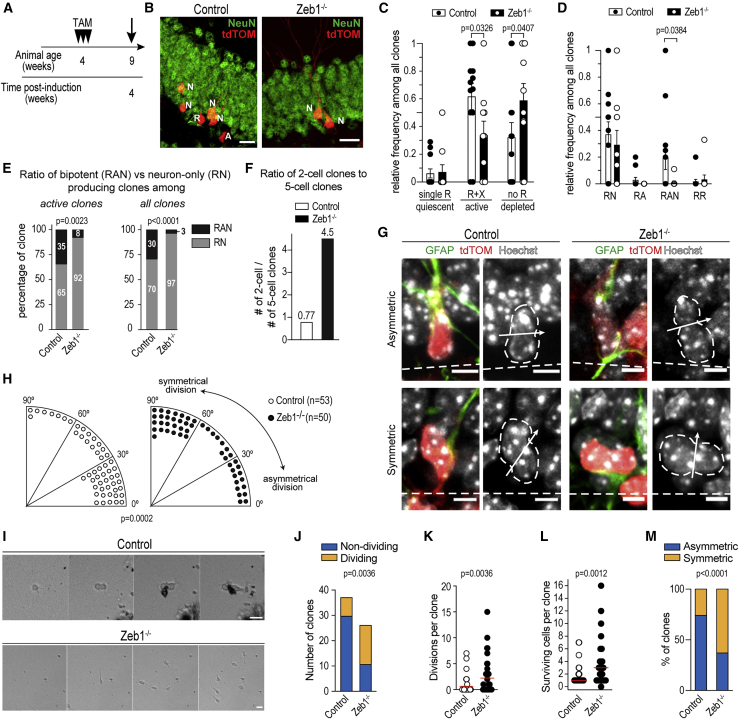
Figure 6.
Analysis of RGL cell clones
(A) Mice were injected with low-dose TAM (0.05 mg), and recombination was assessed 4 weeks post-induction.
(B) Representative images of clones at 4 weeks post-induction.
(C) Relative frequency of quiescent (containing only an RGL cell [single R]), active (containing an RGL cell and any other cell type [R+X]), and depleted (containing only lineage-restricted cells [no R]) clones (n = 38 [control, from 12 hippocampi] versus 35 [Zeb1−/−, from 10 hippocampi]).
(D) Frequencies of active clone subtypes (relative to all clones; n = 26 [control] versus 14 [Zeb1−/−]). Clone subtypes are neurogenic (RGL cell and neurons [RN]), astrogliogenic (RGL cell and astrocyte [RA]), bi-lineage (RGL cell, neuron(s) and astrocyte [RAN]), or self-renewing (two RGL cells [RR]).
(E) Frequencies of bi-lineage (RAN) versus neuron-only-producing (RN) clones across active clones (containing RGL cell; left) and all clones (right).
(F) Ratio of clones containing two cells versus clones containing five cells.
(G) Representative images of cleavage plane orientation in RGL cells undergoing asymmetric (top) or symmetric (bottom) division in control and Zeb1−/− mice. Dashed lines indicate SGZ-hilus border.
(H) Quantification of RGL cell division angles, binned into 30° groups.
(I) Representative images from in vitro time-lapse imaging of primary adult hippocampal cells.
(J) Quantification of dividing versus non-dividing clones.
(K) Numbers of cell divisions per clone.
(L) Numbers of surviving cells per clone.
(M) Ratio of symmetric to asymmetric divisions across all clones.
Dots represent individual clones from 6–7 mice/genotype (C and D), individual cells from 7–8 mice/genotype (H), and individual cells from 5–6 mice/genotype (K and L). Numerical data shown as mean ± SEM. Red line in (K) and (L) represents median. Scale bars: 10 μm (B and G); 20 μm (I). A, astrocyte; N, neuron; R, RGL cell. See also Figure S4.