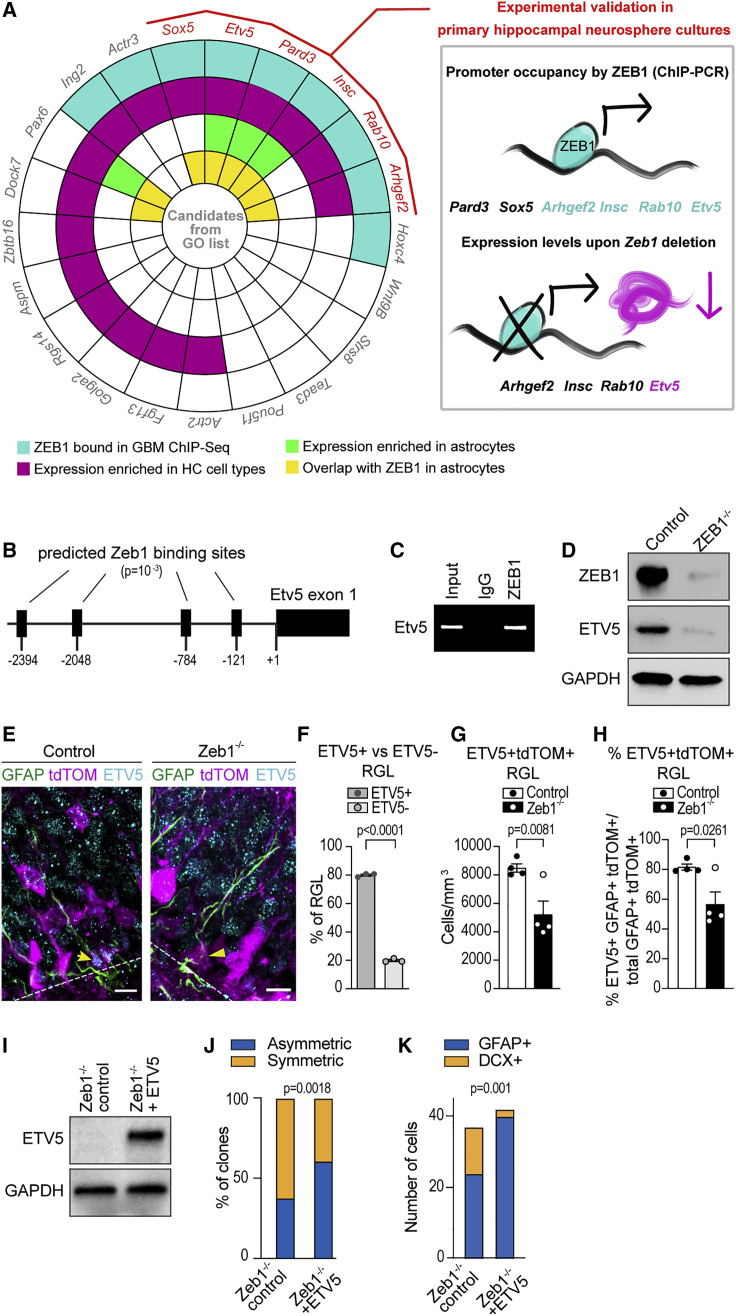
Figure 7.
ZEB1 directly regulates expression of ETV5
(A) Workflow for narrowing down the list of candidates relevant for asymmetric division.
(B) Predicted ZEB1 binding sites with a p value of 10−3 (based on the JASPAR database; Fornes et al., 2020) in the Etv5 promoter region.
(C) ChIP of the Etv5 promoter after pulldown with ZEB1 from hippocampal neurosphere cultures.
(D) Western blot of ETV5 and ZEB1 in hippocampal Zeb1−/− and control neurospheres.
(E) Immunofluorescence staining for ETV5 in RGL cells of control and Zeb1−/− mice.
(F) Quantification of ETV5 expression in control RGL cells.
(G) Quantification of ETV5+GFAP+tdTOM+ cells with RGL morphology in the SGZ at 1 day post-induction.
(H) Percentage of ETV5+GFAP+tdTOM+ RGL cells out of total GFAP+tdTOM+ RGL cells at 1 day post-induction.
(I) Western blot of ETV5 in hippocampal Zeb1−/− neurospheres transduced with a lentiviral ETV5 expression vector and control Zeb1−/− cultures.
(J) Ratio of asymmetric to symmetric divisions quantified from time-lapse imaging of primary adult hippocampal cells.
(K) Quantification of GFAP+ and DCX+ cells after live-cell imaging.
Dots represent individual mice (minimum of two sections analyzed per animal); numerical data are shown as mean ± SEM. Scale bars: 10 μm. GBM, glioblastoma; HC, hippocampus. See also Figure S5 and Table S1.