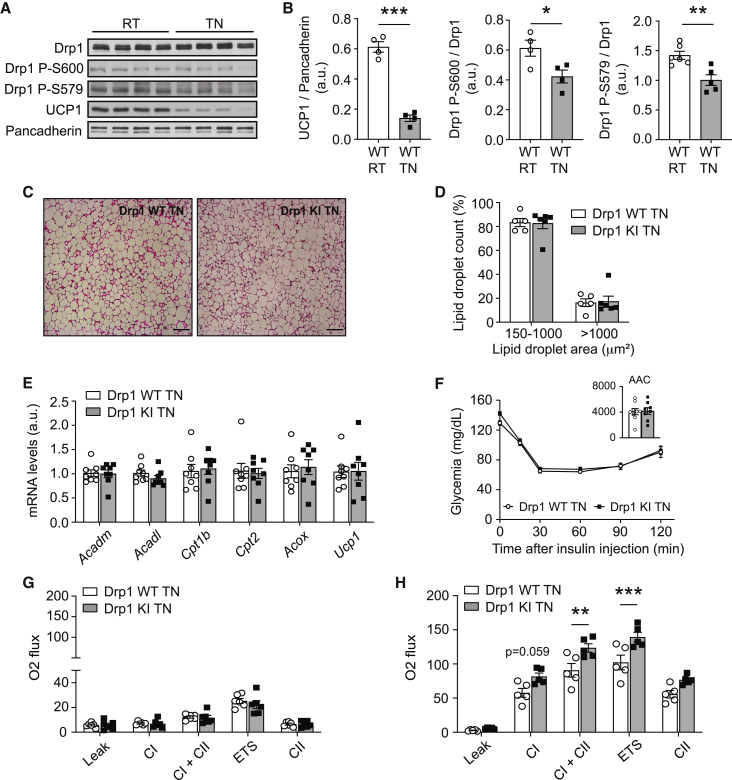
Figure 7.
Thermoneutrality blunts the differences between WT and Drp1 KI mice
WT and Drp1 KI male mice were challenged with a HFD for 4 weeks and housed at thermoneutrality (TN, 30°C–33°C) for an additional 4 weeks before performing the following tests.
(A) Evaluation of total Drp1, Drp1 phosphorylation, and UCP1 protein levels in HFD-fed WT mice housed either at 22°C (RT, room temperature) or at TN.
(B) Quantifications of the markers in (A) (n = 4 per condition).
(C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of BAT from WT and Drp1 KI mice housed at TN (scale bar: 100 μm).
(D) Lipid droplet size quantification from histology images in (C), corresponding to 20 independent images per BAT section (n = 4 samples per genotype).
(E) BAT was collected from WT and Drp1 KI mice and mRNA was extracted to measure fatty acid oxidation and thermogenesis (Ucp1) markers by qPCR.
(F) Insulin tolerance tests performed on HFD-fed WT and Drp1 KI mice housed at TN. Insulin (1 U/kg) was injected and glycemia was measured for the time points indicated.
(G and H) High-resolution respirometry analyses of uncoupled (leak) respiration, CI respiration, CI+CII respiration, maximal ETS capacity, and maximal CII-driven respiration in BAT (G) and liver (H) homogenates from HFD-fed mice housed at TN.
All values are presented as mean ± SEM of n = 10 mice per genotype, unless otherwise stated. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Differences between groups were analyzed using Student’s two-tailed t test in (B), (D), (E), (G), and (H). Linear mixed-effect models were used in (F) to measure time × group interaction effects; subsequent comparisons were performed with Tukey’s honest significant difference post hoc test. See also Figure S7.