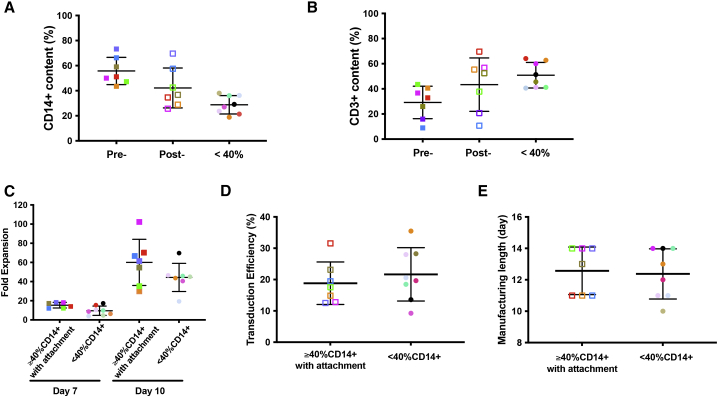
Figure 5.
Case study of CAR T cell manufacturing runs for patients with MM (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03070327; n = 15)
(A) Percentages of CD14+ cells in apheresis products with initially ≥40% CD14+ monocytes pre- (Pre-) and post- (Post-) 2-h plastic adhesion procedure (n = 7), in comparison with the CD14+ monocyte content in apheresis products with initially <40% CD14+ monocytes (<40%) (n = 8). Average CD14+ content by FACS ± SEM is shown for each group, and the groups were compared using Student’s t test. For pre-adhesion versus post-adhesion, p = 0.042; for post-adhesion versus product with initially <40% CD14+ monocytes, p = 0.052. (B) Percentages of CD3+ cells in apheresis products with initially ≥40% CD14+ monocytes before (Pre-) and after (Post-) 2-h plastic adhesion procedure (n = 7), in comparison with the CD3+ cell content of apheresis products with initially <40% CD14+ monocytes (<40%) (n = 8). Average CD3+ content by FACS ± SEM is shown for each group, and the groups were compared using Student’s t test. For pre-adhesion versus post-adhesion, p = 0.046; for post-adhesion versus product with <40% CD14+ monocytes, p = 0.39. (C) Comparison of cumulative fold expansion of total viable cells in CAR T cell manufacturing runs started with apheresis products containing initially ≥40% CD14+ monocytes, which underwent a 2-h plastic adhesion depletion step (n = 7, left group on days 7 and 10), and the manufacturing runs started with apheresis products containing <40% CD14+ monocytes (n = 8, right group on days 7 and 10). Average ± SEM is shown for each group at days 7 and 10 and compared using Student’s t test. On day 7, p = 0.02; at day 10, p = 0.17. (D) Comparison of transduction efficiency between CAR T cell manufacturing runs started with apheresis products containing initially ≥40% CD14+ monocytes, which underwent a 2-h plastic adhesion monocyte depletion step (n = 7) and the manufacturing runs started with apheresis products containing <40% CD14+ monocytes (n = 8). Average transduction efficiency by FACS ± SEM is shown for each group, and the groups were compared using Student’s t test, p = 0.49. (E) Comparison of manufacturing length between CAR T cell manufacturing runs started with apheresis products containing initially ≥40% CD14+, which underwent a 2-h plastic adhesion monocyte depletion step (n = 7) and the manufacturing runs started with apheresis products containing <40% CD14+ monocytes (n = 8). Average manufacturing length ± SEM is shown for each group, and the groups were compared using Student’s t test, p = 0.81. The average length of the runs started from apheresis products with ≥40% CD14+ and monocyte depletion step (12.6 ± 0.57 days) was comparable with that of runs started from apheresis products with <40% CD14+ monocytes (12.4 ± 0.57 days). Each solid-colored square represents an individual apheresis product with initially ≥40% CD14+ monocytes pre-depletion, and the same-colored empty square corresponds to the same product post-depletion. Each solid-colored circle represents an individual apheresis product with initially <40% CD14+ monocytes.