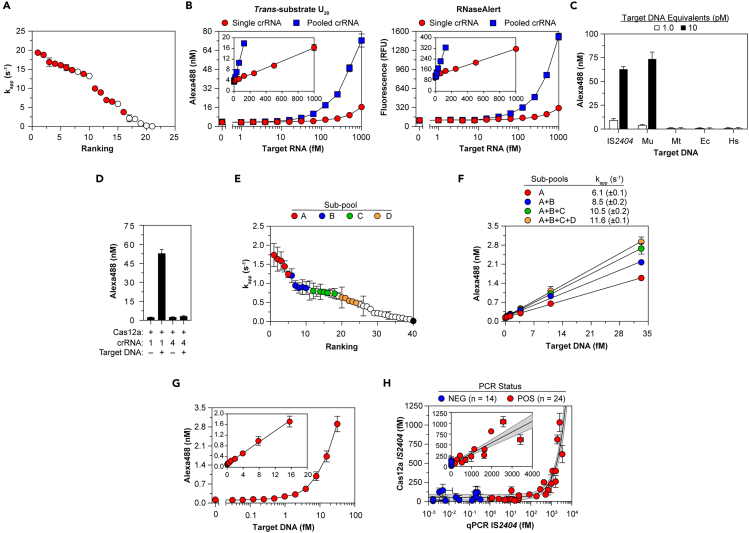
Figure 6.
Pooling of crRNA enables sensitive cas-directed detection of pathogen nucleic acids
(A) Trans-RNase activity of Cas13a bound to individual precursor crRNA, then reacted with target RNA and trans-RNA U10. Filled symbols indicate 13 crRNA selected for pooling. (B) Trans-RNase activity of Cas13a bound to single or 13 pooled crRNA, then reacted with 13 pooled target RNA and U20 (left) or RNaseAlert (right). (Insets) Linear fit to yield kapp (Table S5). (C) Trans-DNase activity of Cas12a bound to crRNA-1, then reacted with IS2404 or genomic DNA and trans-ssDNA C10. Genomic DNA isolated from M. ulcerans (Mu) contains IS2404 protospacers targeted by crRNA-1, whereas genomic DNA isolated from M. tuberculosis (Mt), E. coli (Ec), and humans (Hs) do not. (D) Trans-DNase activity of components tested on C10. Protospacer in target IS2404 complementary to crRNA-1 abuts a PAM, whereas that of crRNA-4 does not. (E) Trans-DNase activity of Cas12a bound to individual crRNA, then reacted with IS2404, which contains protospacers for each crRNA, and C10. Colors indicate 20 crRNA selected for sub-pooling. Activity of Cas12a-crRNA-4 is indicated by black symbol. (F–G) Trans-DNase activity of Cas12a bound to crRNA pools added cumulatively (F) or together (G), then reacted with IS2404 and C10. Linear fits were used to calculate kapp (see Table S5). (H) IS2404 in DNA samples isolated from 38 patient skin swabs quantified by Cas12a trans-activity (y axis) or by qPCR (x axis). Color-coded patient qPCR status was determined from DNA extracted initially at test site. Solid line, detailed in Inset, indicates linear fit to yield kapp (Table S5); gray shading indicates 95% confidence interval. In all panels data represent mean ± SD. See also Figure S6 and Table S5.