Fig. 6. Track KCNE1 and KCNQ1 movements after their ER exit by the ‘retention using selected hook’ (RUSH) strategy.
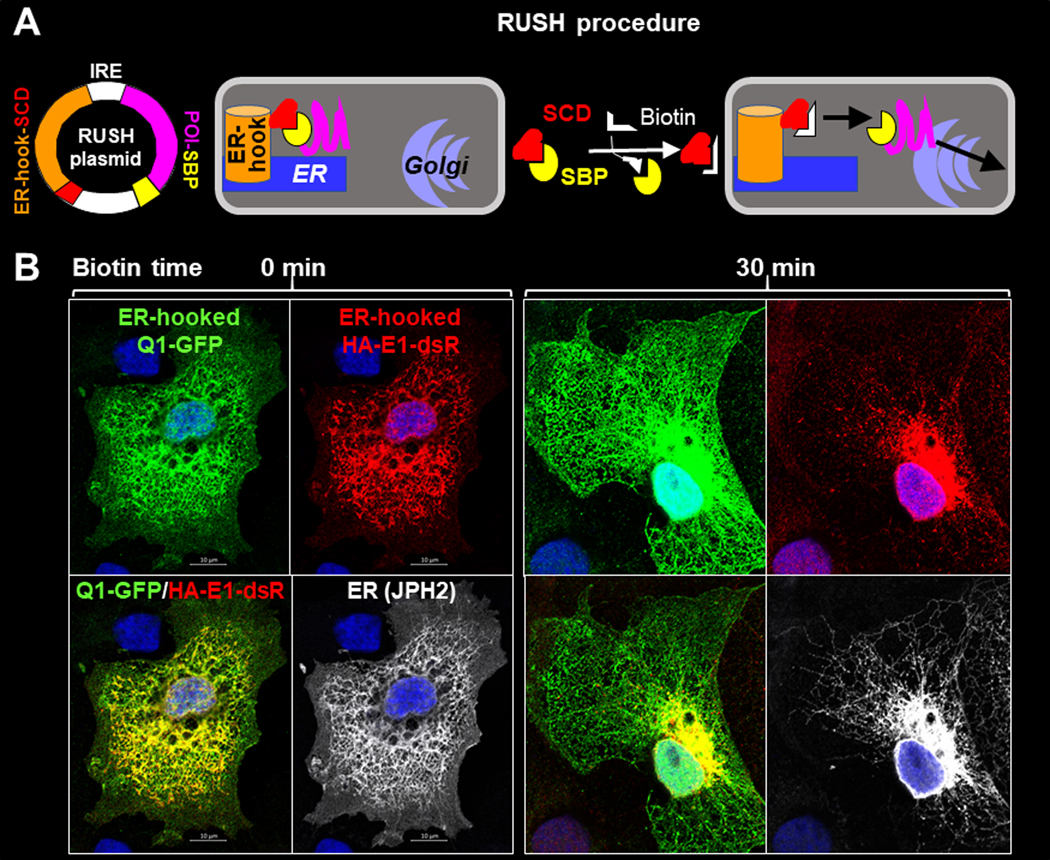
(A) Diagram of RUSH procedure. Protein-of-interest (POI) was fused with a streptavidin-binding-peptide (POI-SBP) and subcloned into a bi-cistronic plasmid (with internal ribosome entry ‘IRE’) that had an upstream ER-resident protein (an isoform of the human invariant chain of the major histocompatibility complex, Ii, retained in the ER membrane by a double arginine motif in its cytoplasmic domain (Boncompain et al., 2012)) fused with ‘streptavidin core domain’ (ER-hook-SCD). POI-SBP and ER-hook-SCD were translated as two independent proteins in the same cells. COS-7 cells were transfected with RUSH plasmid and cultured under the control conditions, during which the POI-SBP was retained at the ER by ER-hook-SCD. Biotin (membrane permeable) added to the culture medium would compete off POI-SBP from the ER-hook-SCD, allowing POI-SBP to exit ER and travel down its secretory path. (B) Fluorescence images of ER-hooked Q1-GFP, HA-E1-dsR and junctophilin-2 (JPH2, an ER marker) in COS-7 cells fixed before (0 min, left) or 30 min (right) after biotin application. Q1-GFP, HA-E1-dsR and JPH2 were detected by GFP mouse Ab/Alexa488 donkey anti-mouse, dsR rabbit Ab/Alexa568 donkey anti-rabbit, and JPH2 goat Ab/Alexa647 chicken anti-goat (pseudo-colored white).
