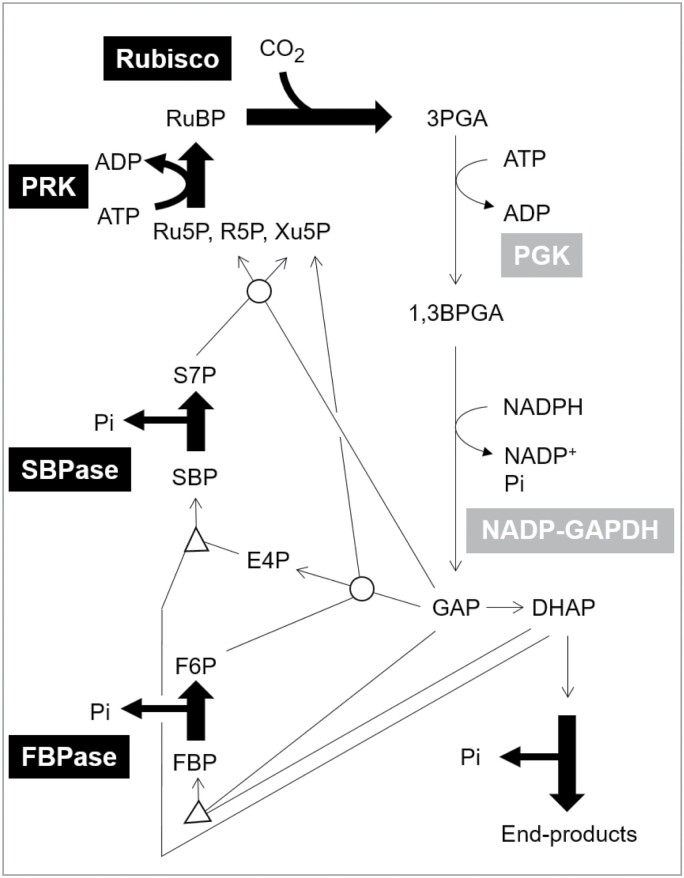
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the Calvin–Benson cycle. This display highlights the location of CBC metabolites and reactions that catalyse irreversible reactions in vivo (thick black arrows; name of enzyme in black box). Reactions that catalyse reversible reactions are shown with thin lines, with the arrow indicating the direction of net flux during operation of the CBC. The enzymes involved in 3PGA reduction are named; the reactions catalysed by transketolase and aldolase are identified by a circle and a triangle, respectively. Triose-P isomerase is indicated with an arrow, and the isomerases that interconvert Xu5P, R5P, and Ru5P are omitted for simplicity, as is the stoichiometry of the reactions. In the absence of photorespiration, the CBC catalyses a net reaction of 6NADPH+9ATP+3CO2→6NADP++9ADP+8Pi+1triose-P. The remaining Pi is recycled during end-product synthesis, which is indicated here schematically for conversion of triose-P (GAP and DHAP) to sucrose. Some end-product synthesis starts from F6P for starch, 3PGA for organic acids, amino-derived amino acids (E4P) for aromatic acids and phenylpropanoids, and pentose-P for nucleotides. Rubisco also catalyses a reaction with oxygen leading to formation of 2PG+3PGA. The 2PG is scavenged by the photorespiration pathway, in which two 2PG are converted to 3PGA with loss of CO2 and NH3. When this happens, the flux in the CBC must be increased relative to end-product synthesis to regenerate the RuBP that is consumed in the oxygenase reaction. Abbreviations: 1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid (1,3BPGA); 3-phosphoglycerate (3PGA); dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP); erythrose 4-phosphate (E4P); fructose 6-phosphate (F6P); fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase); fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP); glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP); glucose 1-phosphate (G1P); inorganic phosphate (Pi); NADP-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NADP-GAPDH); phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK); phosphoribulokinase (PRK); ribose 5-phosphate (R5P); ribulose 5-phosphate (Ru5P); ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP); sedoheptulose 7-phosphate (S7P); sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase (SBPase); sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate (SBP); xylulose 5-phosphate (Xu5P).