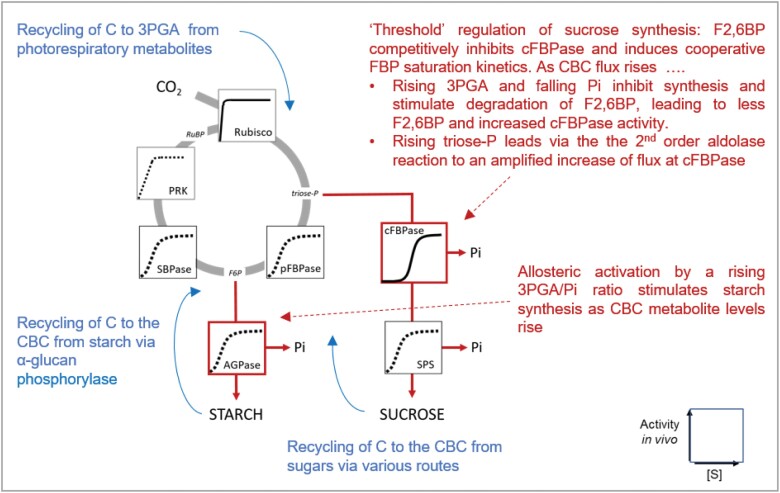
Fig. 7.
Tight regulation of net carbon maintains CBC metabolites at substantial levels in low light and low CO2, allows a rapid increase in net product synthesis as CBC metabolite rise, and maintains levels of metabolites to support CBC flux and energy dissipation via photorespiration in low CO2. This is achieved by tight regulation of end-product synthesis (red) and probably by recycling of carbon to the CBC (blue). In steady-state photosynthesis, five out of six of the triose-Ps must be used to regenerate RuBP (actually, more if photorespiration is occurring) and the remainder can be used for end-product synthesis, which recycles Pi and allows continued ATP synthesis. If end-product synthesis is too fast, RuBP will be deleted and CO2 fixation will be inhibited. If end-product synthesis is too slow, ATP synthesis will be restricted and CO2 fixation inhibited. Sucrose synthesis is regulated by a network including F2,6BP according to a ‘threshold’ principle that inhibits removal of triose-P by cFBPase when triose-P and other CBC metabolites fall below a ‘threshold’ level, and facilitates a steep rise in flux as net CO2 fixation rises and CBC metabolites rise above this threshold (see Stitt, 1990 and Stitt et al., 2010 for details). Starch synthesis is stimulated by allosteric activation of AGPase as the CBC metabolite levels rise and Pi falls. At the same time, falling CBC metabolite levels may trigger recycling of carbon from starch and sugars (for details, see text). A short-term shortfall of carbon in the CBC may also be buffered by carbon returning to 3PGA from the large pools of photorespiratory metabolites. The sketch of pathways is modified from Stitt et al. (2010). Abbreviations: ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase); cytosolic/plastidic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (c/pFBPase); fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP); F2,6BP, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate; inorganic phosphate (Pi); phosphoribulokinase (PRK); substrate concentration ([S]), sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase (SBPase); sucrose-phosphate synthase (SPS). Metabolite abbreviations are as in Fig. 1.