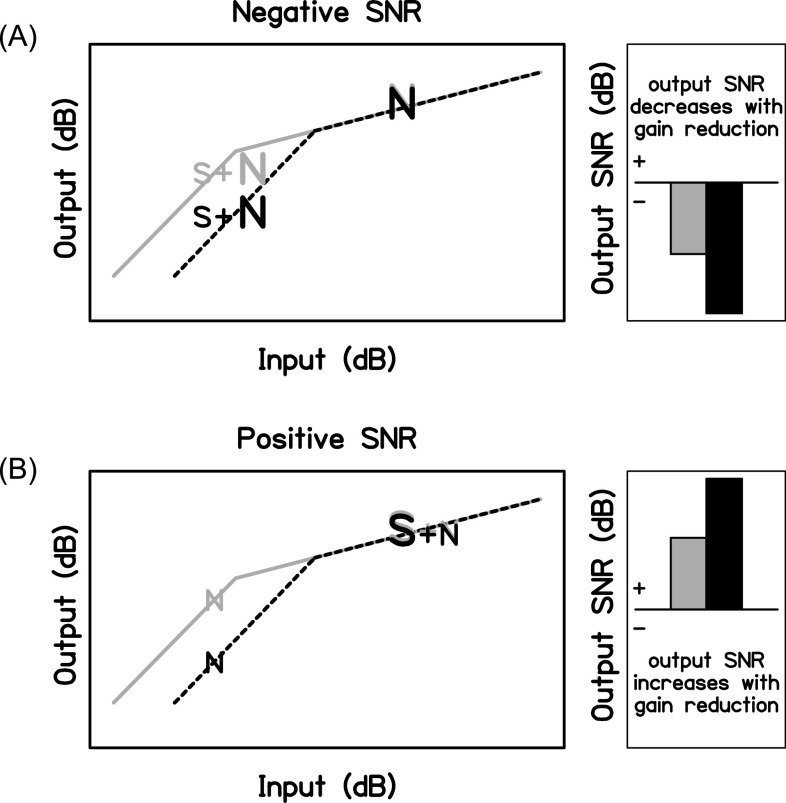
FIG. 1.
Schematics of the hypothesized relationship between the SNR and gain reduction. The left panels show the cochlear input-output function with full gain (gray solid lines) and gain reduction (black dotted lines). Gain reduction reduces the output level of the lower-level input: speech-in-noise at a negative SNR (A) and noise in the dips of the speech at a positive SNR (B). The right panels show the overall output SNR for these scenarios. Compared to full gain (gray bars), output SNR is hypothesized to decrease with gain reduction (black bars) for a negative SNR (A) and increase with gain reduction for a positive SNR (B).