FIGURE 6.
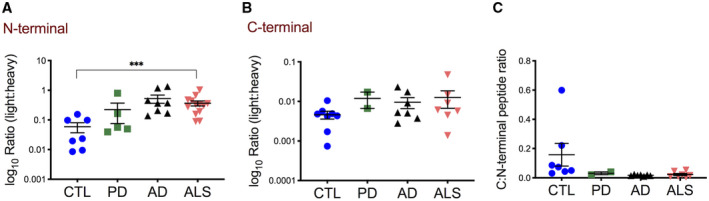
The C to N‐terminal TDP‐43 peptide ratio was not increased in ALS spinal cord urea fractions. (A and B) Shown are absolute abundances of light peptides (log10 ratio (light:heavy peptide)) (A) In contrast to motor and prefrontal cortex urea fractions the N‐terminal peptide was increased in ALS compared to CTL (n = 8) (***p = 0.0001), but not in ALS (n = 16) compared to PD (n = 8) and AD (n = 8) (p = 0.14 and p = 0.88). (B) The C‐terminal peptide was unaltered in ALS compared to all other diagnostic groups (CTL p = 0.3, PD and AD p = 0.9). (C) The calculated C:N‐terminal peptide ratio was unaltered in ALS compared to CTL (p = 0.1), PD or AD (both p = 0.9). One‐way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test
