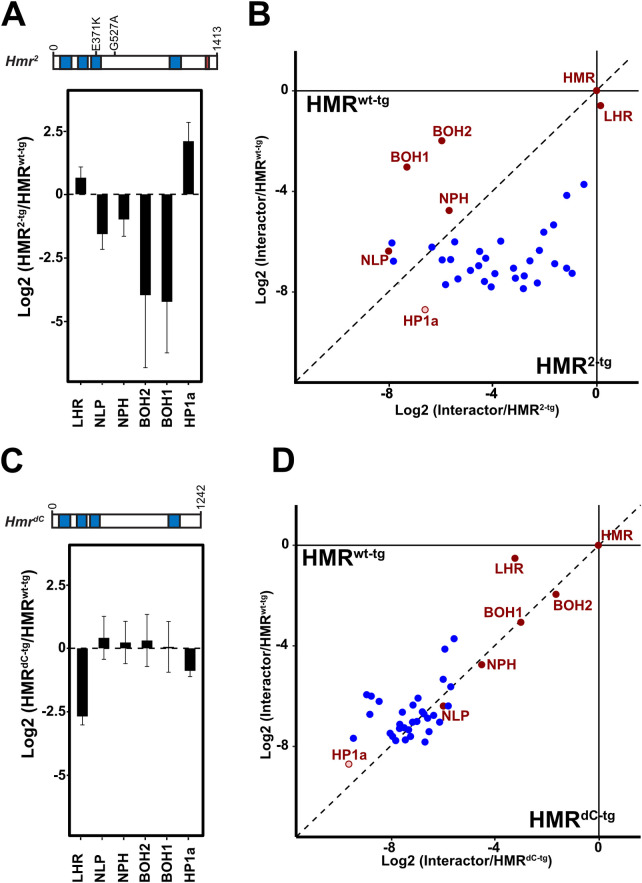
Fig 3. Two different Hmr mutations interfere differently with HMR interactome and HMR complex formation.
Effect of Hmr2-tg (A) and HmrdC-tg (C) mutations on the HMR interaction with the HMR complex components and HP1a. Y-axis represents the Log2 fold-change of HMR2-tg/HMRwt-tg and HMRdC-tg/HMRwt-tg, respectively, calculated after normalization of each sample to the enrichment of the HMR protein used as bait. Error bars reflect the SEM (HMRwt-tg: n = 9; HMRdC-tg: n = 10, HMR2-tg: n = 3). Differential interaction proteome between ectopically expressed wild type or mutated HMR (HMRwt-tg versus HMR2-tg (B) or HMRwt-tg versus HMRdC-tg (D)). Only proteins enriched in HMRwt-tg or HMRendo vs CTRL(p < 0.05) are shown. Components of the HMR complex are shown in red, all other factors in blue. To display the differences within each interactome, the enrichment of each putative interactor was normalized to the enrichment of the HMR protein used as bait. The resulting values were then plotted against each other. Dots above the diagonal indicate a stronger enrichment in the HMRwt-tg pull down, dots below the diagonal a stronger enrichment in the HMR mutated alleles (HMR2-tg or HMRdC-tg). All proteomic data are available at the PRIDE partner repository [39] Further details are available in S3 Table.