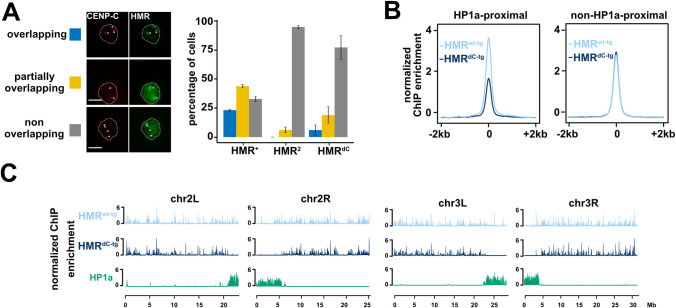
Fig 4. The HMR C-terminus is required for HMR localization in proximity to centromeres and HP1a-bound chromatin.
(A) Ectopic HMRdC-tg fails to form bright (peri)centromeric foci in SL2 cells. Immunofluorescence images of cells expressing different Hmr transgenic alleles (HA-Hmrwt-tg, HA-HmrdC-tg or HA-Hmr2-tg) together with wild type LHR showing the co-staining of HA-HMR and CENP-C. Based on the overlap between HMR and CENP-C signals, cells were categorized in three groups (overlapping (blue), partially overlapping (yellow) and non-overlapping (grey)) and the number of cells belonging to each group quantified. The nuclear boundary is indicated by the white dashed line and the centromeres (as identified by a-CENP-C staining) by white arrows. Error bars represent standard error of the means (n = 2). Size bars indicate 5 μm. (B) HP1a-proximal binding is specifically disrupted in HMRdC-tg. Average plot of FLAG-HMR ChIP-seq profiles (z-score normalized) centred at high confidence FLAG-HMR peaks in 4 kb windows. HP1a-proximal (left) and non-HP1a-proximal (right) peaks are shown for HMRwt-tg (light blue) and HMRdC-tg (dark blue). (C) HMRdC-tg genome-wide binding is impaired in proximity to centromeres and mostly unaffected at chromosome arms. Chromosome-wide FLAG-HMR ChIP-seq profiles (z-score normalized) for HMRwt-tg (light blue), HMRdC-tg (dark blue) and HP1a (green). Chromosomes 2L, 2R, 3L and 3R are shown. Pericentromeric heterochromatin is marked by HP1a enriched territories distal (2L/3L) or proximal (2R/3R) to the respective x-axis. Plots in (B) and (C) represent an average of 5 biological replicates of FLAG-HMR ChIP-Seq in SL2 cells.