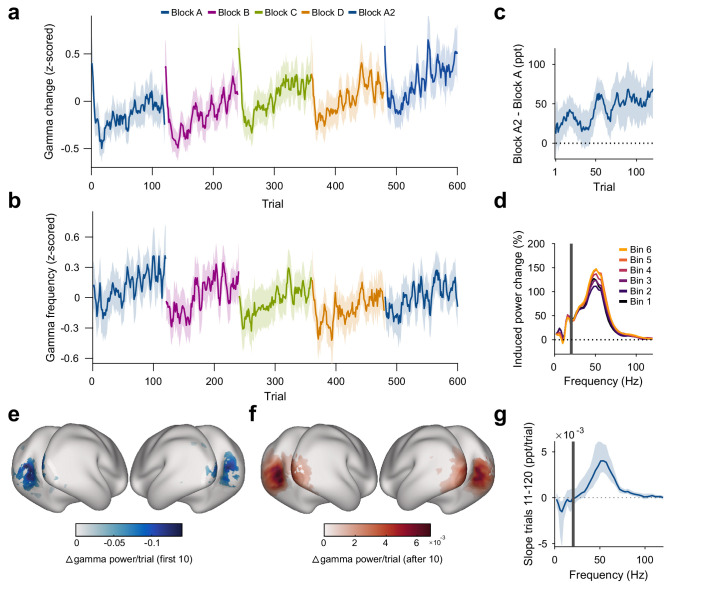
Figure 3. Repetition effects on gamma power and peak frequency are stimulus specific.
(a) Stimulus-induced gamma power in V1/V2, on a per-trial basis. (b) Peak frequency of stimulus-induced gamma in V1/V2, on a per-trial basis. Values in (a, b) were z-scored within subjects. (c) Within-subject differences in stimulus-induced V1/V2 gamma power between the second and the first block of a given oriented grating (A2 minus A). Note that induced gamma power also showed an increase with stimulus-independent trial number, which is controlled for in the regression model presented in Results. In (a–c), the average and the 95% bootstrap confidence intervals were computed using a five-trial-wide running window. (d) Stimulus-induced power-change spectra in V1/V2 during the 120 presentations of a given stimulus, plotted in sequential 20-presentation bins. Power values from 1 to 20 Hz (left of the gray bar) were computed using Hann tapering, power values of higher frequencies were computed using multi-tapering. Line noise was removed using DFT filters. (e) Spatial distribution of the early gamma power decrease: For each cortical dipole, a regression line was fit to induced gamma power as a function of stimulus repetitions 1–10. Subject-averaged slopes (significance-masked, tmax-corrected) are shown. (f) Spatial distribution of the late gamma increase: For each cortical dipole, a regression line was fit to induced gamma power as a function of stimulus repetitions 11–120. Subject-averaged slopes (significance-masked, tmax-corrected) are shown. In (e, f), black-to-white shading indicates areas V1, V2, V3, V3A, and V4. (g) For each frequency, a linear regression across repetitions was fit to the per-trial visually induced power change in V1/V2 during the late trials (trials 11–120). Average slope and 95% bootstrap CI over subjects is shown. The corresponding analysis for the early trials (trials 1–10) is shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1d. All results in this figure show averages over all participants.