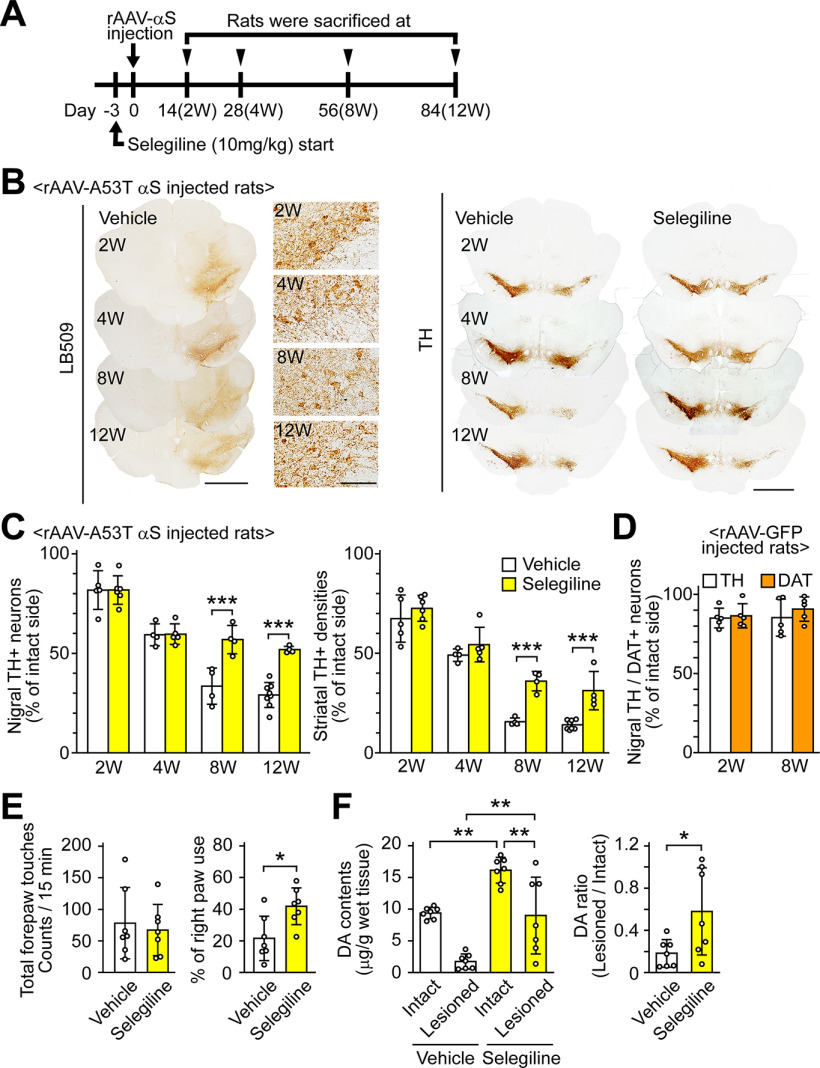
Figure 6.
MAO-B inhibition attenuates α-syn-induced dopaminergic neuronal loss in rats. A, Experiment schedule. Selegiline was resolved in saline before use. The selegiline solution was subcutaneously injected at a dose of 10 mg/kg once daily from 3 d before the viral injection to the day before killing. As a control, the same volume of vehicle was simultaneously injected in a separate set of rats. Rats were killed at two weeks (vehicle, n = 5; selegiline, n = 6), four weeks (vehicle, n = 4; selegiline, n = 5), eight weeks (vehicle, n = 4; selegiline, n = 4), and 12 weeks (vehicle, n = 8; selegiline, n = 4) after rAAV-A53T α-syn injection. B, Immunohistochemical analysis of rat midbrains injected rAAV-A53T α-syn. Left panels show anti-human α-syn antibody (LB509)-stained images at low (scale bar: 2 mm) and high magnifications (scale bar: 100 μm). Right panels show anti-TH antibody-stained sections (scale bar: 2 mm). C, Assessment of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuronal damage by rAAV-A53T α-syn injection. Left graph shows percentages of the remaining nigral TH-positive neurons in the lesioned sides to those in the intact sides. A two-way ANOVA demonstrated significant main effects for the drug (F(1,32) = 26.901, p < 0.001) and for time (F(3,32) = 75.607, p < 0.001), with a significant drug × time interaction (F(3,32) = 8.814, p < 0.001). In the vehicle-treated rats, the numbers of TH-positive neurons in intact sides were 25,265.0 ± 1306.5 and 21,855.8 ± 4146.9 at 8 and 12 weeks after viral injection, respectively. In the selegiline-treated rats, the numbers of TH-positive neurons in intact sides were 19,553.9 ± 3387.2 and 21,484.0 ± 2388.3 at 8 and 12 weeks after viral injection, respectively. Right graph shows percentages of the remaining TH-positive fibers in the striatum. A two-way ANOVA demonstrated significant main effects for the drug (F(1,32) = 75.728, p < 0.001) and for time (F(3,32) = 141.373, p < 0.001), with a significant drug × time interaction (F(3,32) = 16.381, p < 0.001). D, Assessment of nigral dopaminergic neuronal damage by rAAV-GFP injection. Rats were killed two and eight weeks later (n = 5 per group). Graph shows percentages of remaining nigral TH or DAT-positive neurons in the lesioned sides to those in the intact sides. E, Assessment of motor impairment by rAAV-A53T α-syn injection (n = 7 per group). Cylinder test was performed at eight weeks after rAAV-A53T α-syn injection. Left and right graphs show total forepaw touches and percentages of right paw touches to total paw ones, respectively. F, Striatal DA contents at eight weeks after rAAV-A53T α-syn injection (n = 7 per group). Left and right graphs show the striatal DA contents and the ratios of DA contents in the lesioned sides to those in the intact sides, respectively. Data represent mean ± SD and were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test (C), unpaired t test (E and right graph of F), and one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test (F, left graph). Data represent mean ± SD; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Dopamine, DA; dopamine transporter, DAT; α-syn, αS; tyrosine hydroxylase, TH.