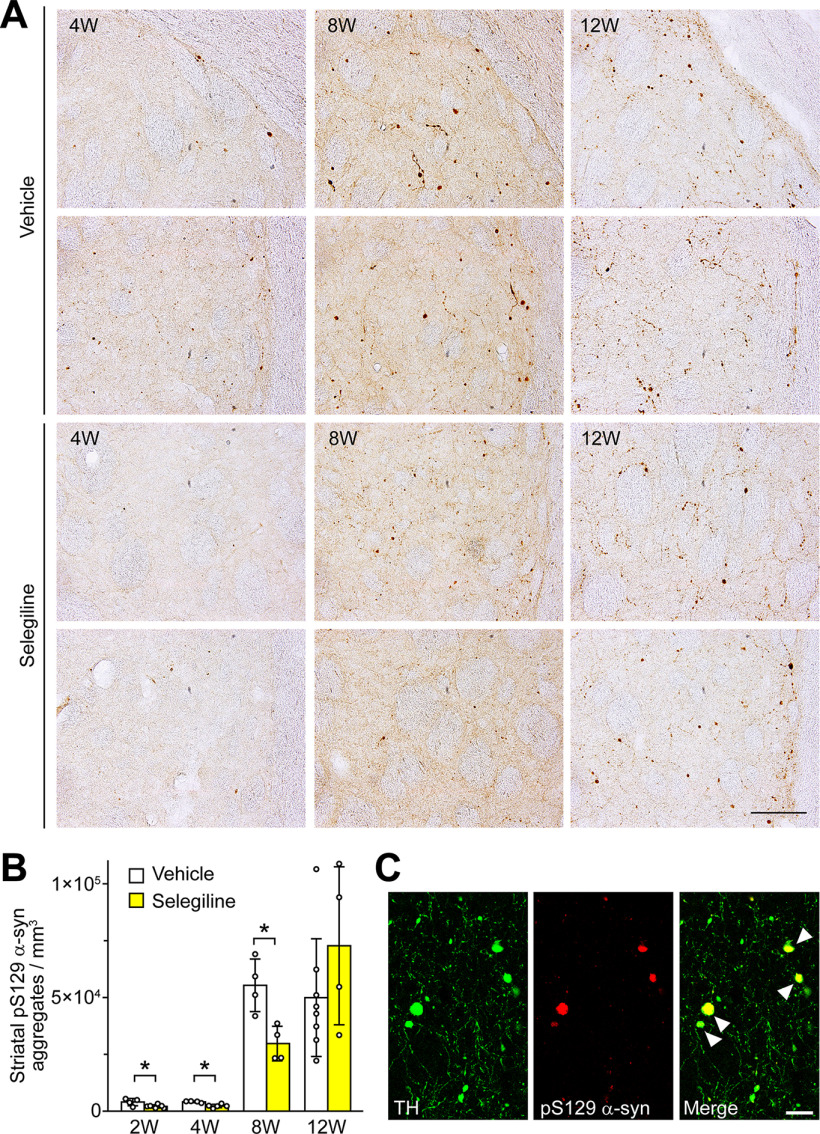
Figure 7.
MAO-B inhibition delays the formation of pS129 α-syn aggregates. Rats were killed at two weeks (vehicle, n = 4; selegiline, n = 6), four weeks (vehicle, n = 4; selegiline, n = 5), eight weeks (vehicle, n = 4; selegiline, n = 4), and 12 weeks (vehicle, n = 8; selegiline, n = 4) after rAAV-A53T α-syn injection. A, Immunohistochemical analysis of striatal pS129 α-syn aggregates. Micrographs show pS129 α-syn aggregates of upper and middle portions of the dorsal lateral striatum at 4, 8, and 12 weeks after viral injection. Scale bar: 100 μm. B, Graph shows the number of pS129 α-syn aggregates. A two-way ANOVA demonstrated significant main effects for the drug (F(1,31) = 8.619, p = 0.006) and for time (F(3,31) = 162.594, p < 0.001), with a significant drug × time interaction (F(3,31) = 4.204, p = 0.013). Data were log-transformed and analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test. Data represent mean ± SD; *p < 0.05. C, Immunofluorescent analysis of striatal pS129 α-syn aggregates at 12 weeks after rAAV-A53T α-syn injection. Left and middle micrographs show the sections stained with anti-TH (green) and anti-pS129 α-syn (red) antibodies, respectively. Right micrograph shows the merged image. Arrowheads indicate TH-positive and pS129 α-syn-positive aggregates. Scale bar: 25 μm. Tyrosine hydroxylase, TH.