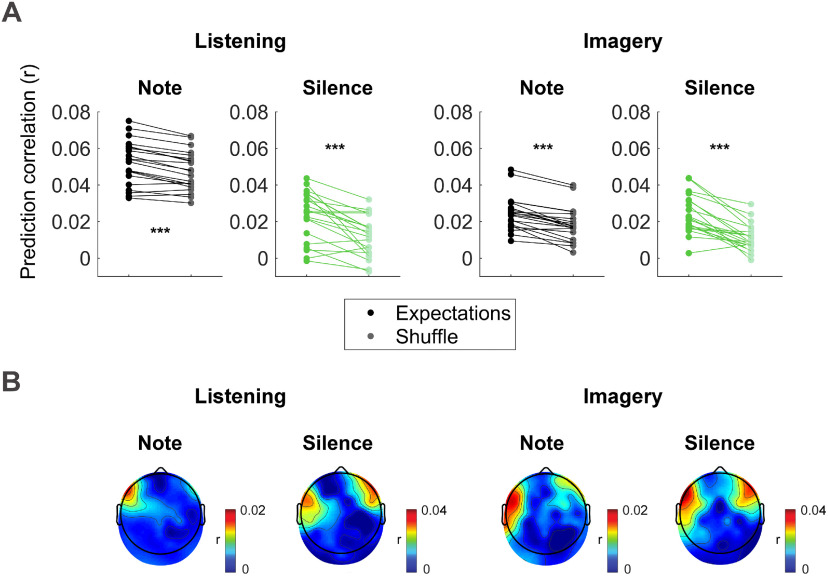
Figure 5.
Notes and silence expectation encoding in low-frequency EEG. A multivariate TRF analysis was conducted to identify the linear transformation that best predicts low-frequency EEG data (0.1–30 Hz) based on a three-dimensional stimulus representation indicating for either note or silent-events the event onset time, entropy at that position, and surprise of that event. A, EEG prediction correlations (r) of the TRF using the note or silence expectation values estimated with IDyOM are compared with a null model, where the EEG prediction correlations were obtained with a TRF that was fit after a random shuffling of the expectation values (event onset times were preserved). Results averaged across all electrodes are reported for both listening and imagery conditions. Each dot indicates the result for a single subject. Significant differences were measured for notes and silent-events in both conditions (permutation test, ***p < 10−4). B, Topographical maps indicating the EEG prediction correlation increase (expectation minus null model) at each EEG channels.