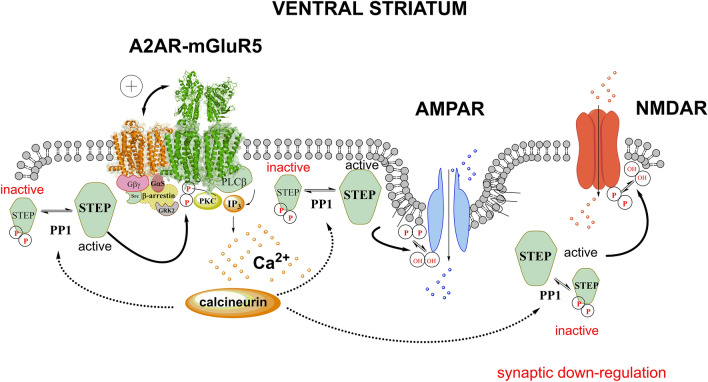
Fig. 1.
Cocaine, A2AR and STEP interactions activating STEP in the ventral striatum can be increased through enhanced allosteric receptor-receptor interactions in A2AR-mGluR5 heteroreceptor complexes in the ventral striatal-pallidal GABA neurons with A2AR protomer (orange color) activation increasing mGluR5 protomer (green color) signaling. The Gq activation results in increased PLC beta activity leading to a rise of intracellular calcium levels via improved IP3 levels and increased activation of calcineurin. Its phosphatase activity in turn activates PP1 which then via dephosphorylation activates STEP. Activated STEP bound to AMPAR and NMDAR can then inactivate these excitatory synaptic glutamate receptors via dephosphorylation followed by their internalization. A dynamic synaptic downregulation develops. To the left part of the figure, it is shown that this dynamic process can be counteracted by PP1induced activation of STEP bound to mGluR5 leading to its inactivation. The reduction of the mGluR5 signaling can then reduce the process of activated STEP binding to AMPAR and NMDAR with a return of excitatory synaptic signaling