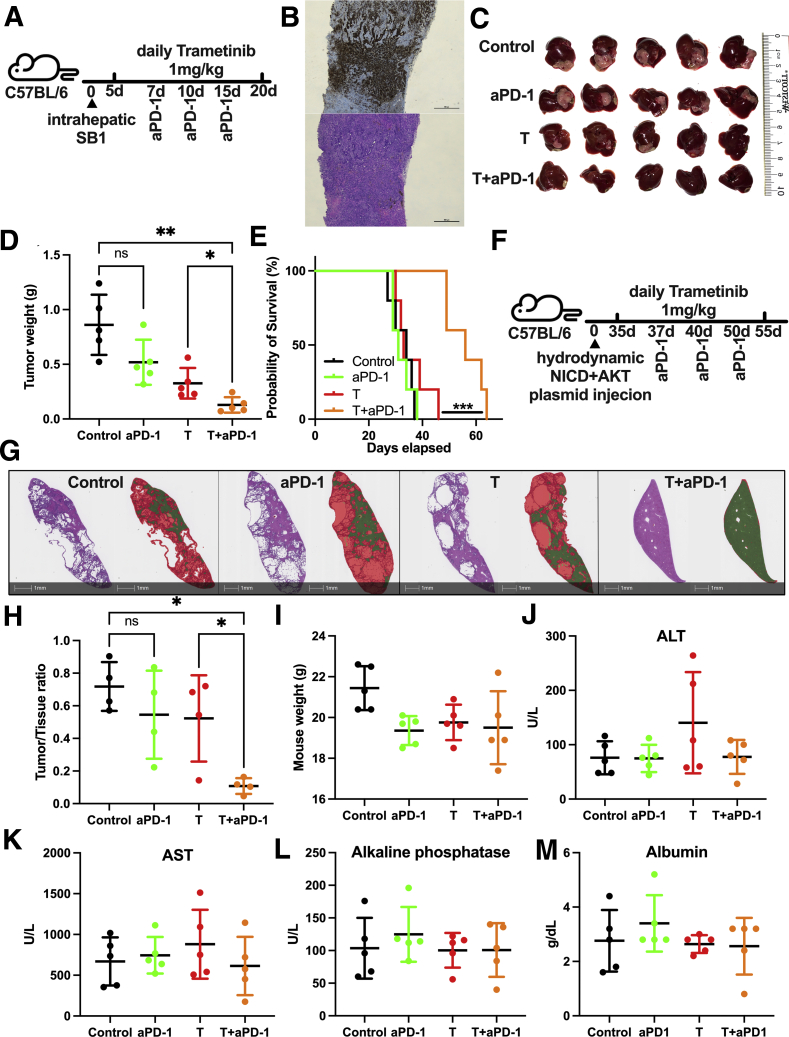
Figure 4.
Trametinib in combination with anti–PD-1 controls tumor growth in orthotopic iCCA models. (A) Experimental set-up: C57BL/6 mice with intrahepatic injection of 2 × 105 SB1 cells treated with trametinib by daily gavage and received anti–PD-1 (200 μg/mouse at the indicated time points). (B) Representative images of CK19 staining (upper section) and H&E staining (lower section) of intrahepatic SB1 tumors. Scale bar: 500 μm. (C) Representative pictures of intrahepatic SB1 tumors. Experimental set-up is shown in Figure 4A. (D) Tumor weights (g) of intrahepatic SB1 tumors. Experimental set-up is shown in Figure 4A. (E) Survival of mice with intrahepatic SB1 tumors over time (n = 5 per group), log-rank test. (F) Experimental set-up: C57BL/6 mice with hydrodynamic tail vein injection of NICD + AKT plasmid injection treated with trametinib by daily gavage and received anti–PD-1 (200 μg/mouse at the indicated time points). (G) Whole slide scan of a representative H&E stain (sections on the left) of a murine iCCA-bearing liver and tissue section after image analysis using HALO Random Forrest Classifier function (Indica Labs, Albuquerque, NM) and shown as a digital overlay indicating areas classified as tumor (red) and remaining normal liver (green). Scale bar: 1 mm. (H) Tumor to liver tissue ratio after NICD + AKT injection (n = 4 per group) corresponding to Figure 4F. Experimental set-up is shown in Figure 4A. (I) Weight of mice after treatment. Experimental set-up is shown in Figure 4E. (I) Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), (J) aspartate aminotransferase (AST), (K) alkaline phosphatase, and (L) albumin serum levels after treatment. Experimental set-up is shown in Figure 4A. Data represent means ± SD. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01; Student t test. aPD-1, anti-Programmed cell death protein-1; T, trametinib.