Figure 2.
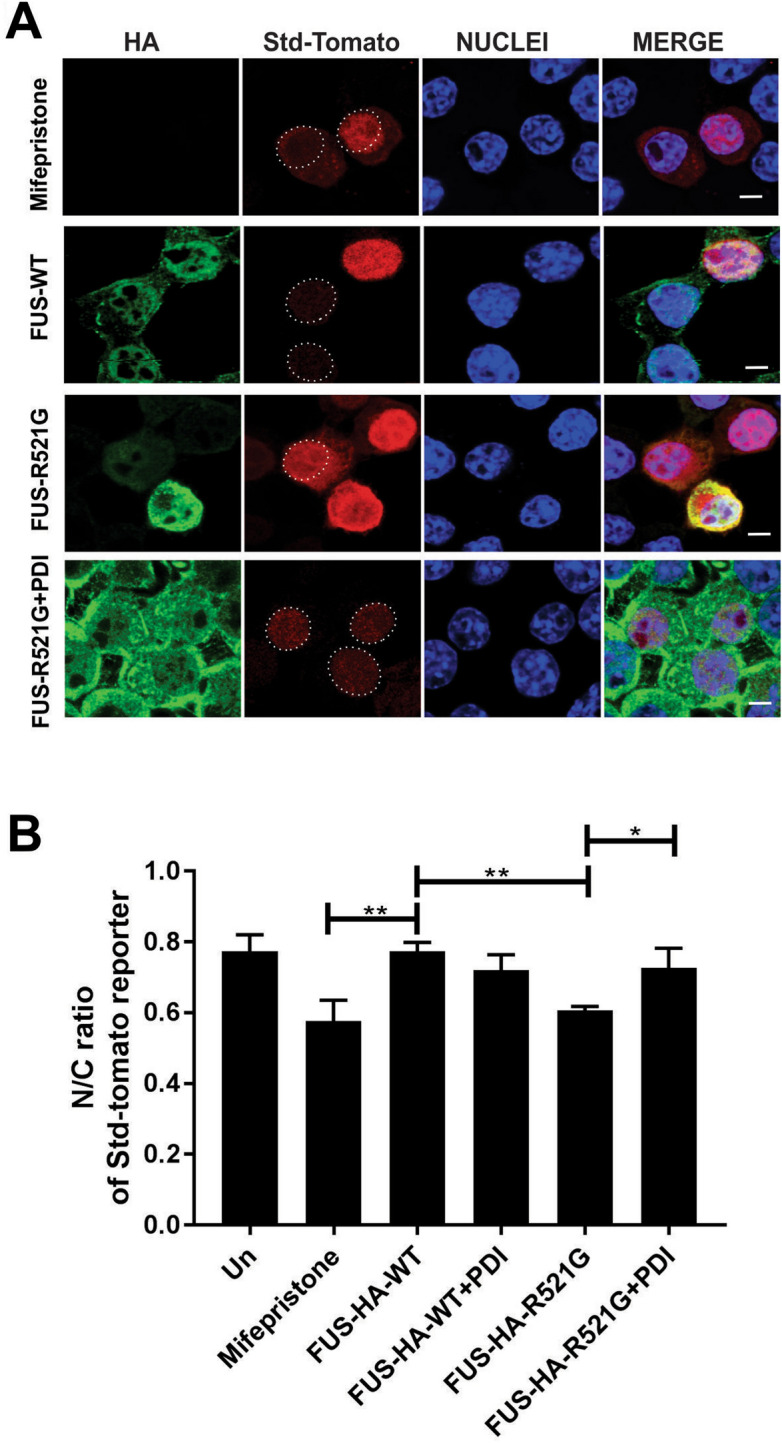
Over-expression of PDI is protective against inhibition of nuclear import induced by mutant FUS in a neuronal cell line. (A) Fluorescent microscopy images of cells 48 h post-transfection, expressing FUS-HA, NES-tdTomato-NLS (Std-Tomato) and either PDI or empty vector following immunocytochemistry in Neuro-2a cells. Cells transfected with 1 µm Mifepristone (row 1), FUS-HA-WT (row 2), mutant FUS-HA-R521G with empty vector (row 3) or mutant FUS-HA-R521G co-expressing PDI (row 4). Scale bar = 5 µm. (B) Quantification of the nuclear to cytoplasmic (N/C) fluorescence intensity ratio of Std-Tomato in Neuro-2a cells expressing FUS-HA-WT or mutant FUS-HA-R521G or co-expressing PDI in (A). Significantly more cytoplasmic reporter is present in cells expressing mutant FUS-HA-R521G (**p < 0.05) compared to FUS-HA-WT. However, co-expression of PDI (*p < 0.05) results in more reporter localised in the nucleus in FUS-HA-R521G cells compared to those expressing empty vector. Values represent mean ± SD, n = 3. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
