Figure 4.
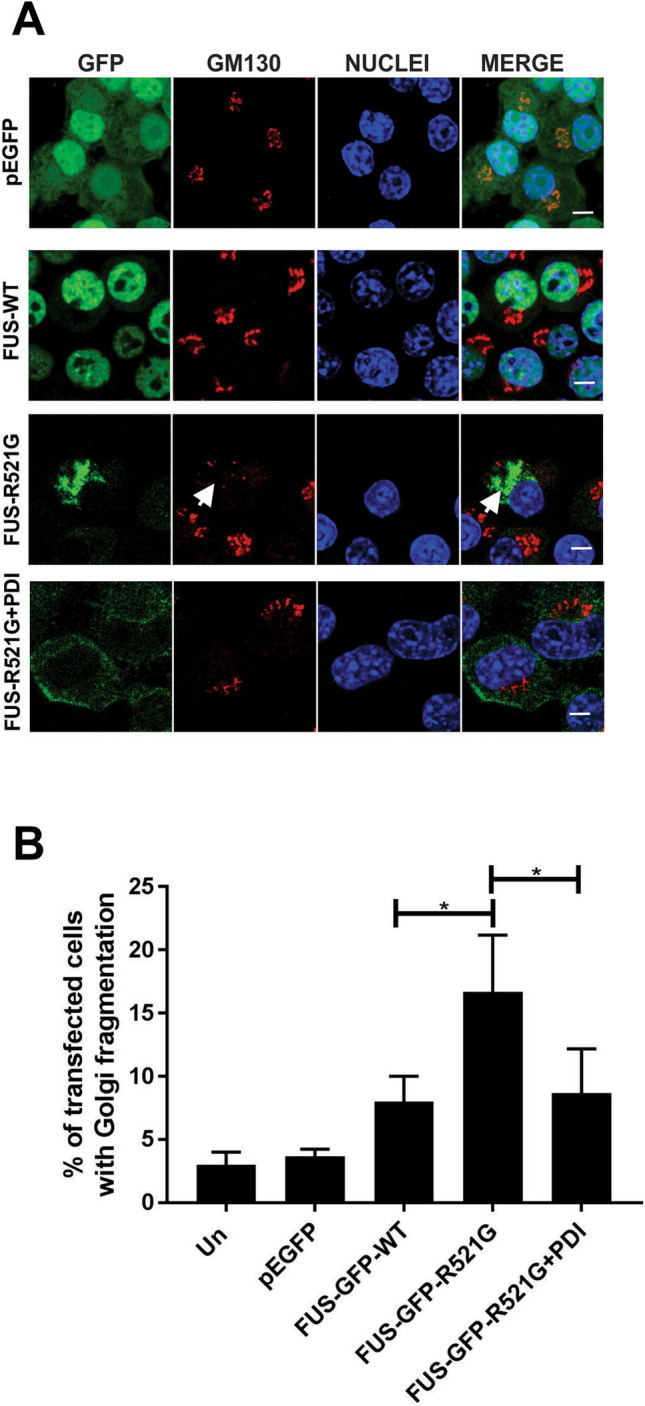
Over-expression of PDI is protective against mutant FUS induced Golgi fragmentation in a neuronal cell line. (A) Neuro-2a cells co-expressing EGFP (row 1), FUS-GFP-WT (row 2) or mutant FUS-GFP-R521G with either empty vector, (row 3) or PDI (row 4) at 72 h post-transfection, were subjected to immunocytochemistry for Golgi marker GM130 and counter-staining with Hoechst 33342 stain (nuclei). Most cells expressing EGFP, or FUS-GFP-WT (row 1 and 2) contained an intact Golgi apparatus. Conversely, cells expressing mutant FUS-GFP-R521G with empty vector displayed fragmented Golgi, indicated with white arrows (row 3). However, over-expression of PDI reduced Golgi fragmentation in these cells (row 4). Scale bar = 5 µm. (B) Quantification of cells in (A). A significant reduction (*p < 0.05) in the proportion of cells with Golgi fragmentation was observed in cells expressing mutant FUS-GFP-R521G with PDI, compared to those expressing mutant FUS with vector only. Values represent mean ± SD, n = 3. *p < 0.05.
