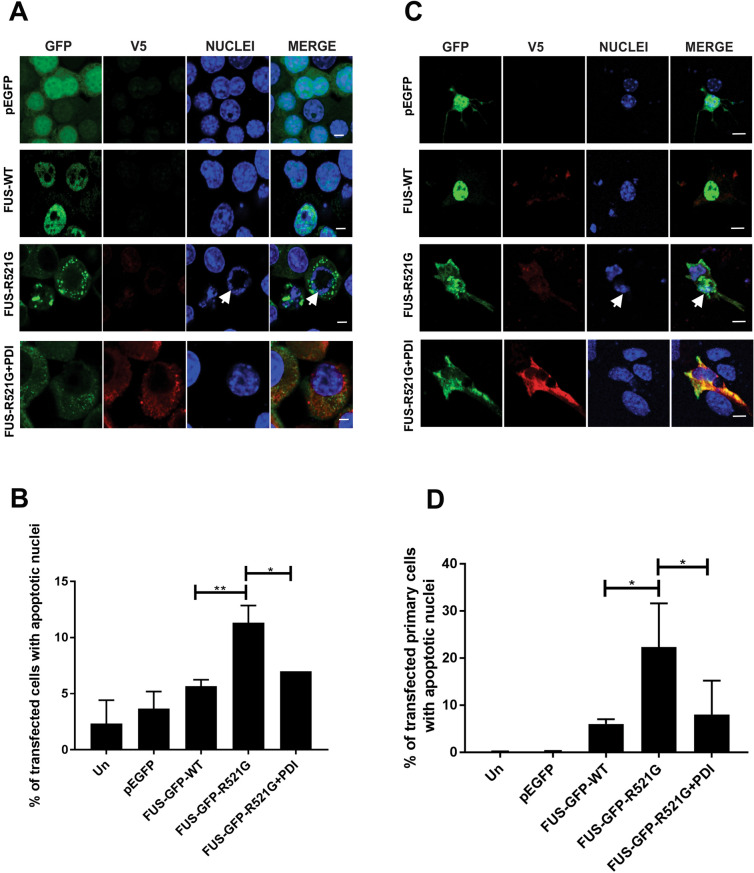
Figure 6.
Over-expression of PDI is protective against mutant FUS-induced apoptosis in a neuronal cell line and primary cultures. (A) Neuro-2a cells co-expressing EGFP, FUS-GFP-WT or FUS-GFP-R521G with PDI, were examined by confocal microscopy at 72 h post-transfection following nuclei staining using Hoechst 33342 (blue). White arrows represent condensed or fragmented nuclei, indicating that apoptosis is underway. Few untransfected cells or those expressing EGFP (row 1) or FUS-GFP-WT (row 2) contained fragmented nuclei (< 5%), but more cells expressing FUS-GFP-R521G with empty vector (row 3) displayed Hoechst-stained condensed nuclei, indicating induction of apoptosis. Fewer cells co-expressing FUS-GFP-R521G with PDI (row 4) were undergoing apoptosis compared to those co-expressing mutant FUS with empty vector. Scale bar = 5 µm. (B) Quantification of apoptotic nuclei in cells in (A) expressing FUS and PDI. Over-expression of PDI with FUS-GFP-R521G resulted in significantly fewer cells with apoptotic nuclei compared to cells transfected with empty vector only (*p < 0.05). A significant difference was also observed between FUS-GFP-WT and mutant FUS-GFP-R521G (**p < 0.01) expressing cells. (C) Mouse primary cells co-expressing EGFP only (row 1), FUS-GFP-WT (row 2) or FUS-GFP-R521G with empty vector (row 3), with PDI (rows 4) and counter staining with Hoechst 33342 stain to visualise apoptotic nuclei, indicated by white arrows. Scale bar = 10 µm. (D) Quantification of apoptotic nuclei in cells in (C) expressing FUS and PDI. Significantly fewer cells were apoptotic when PDI was co-expressed with FUS-R521G (*p < 0.05) compared to those expressing vector only. Values represent mean ± SD, n = 3 **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.