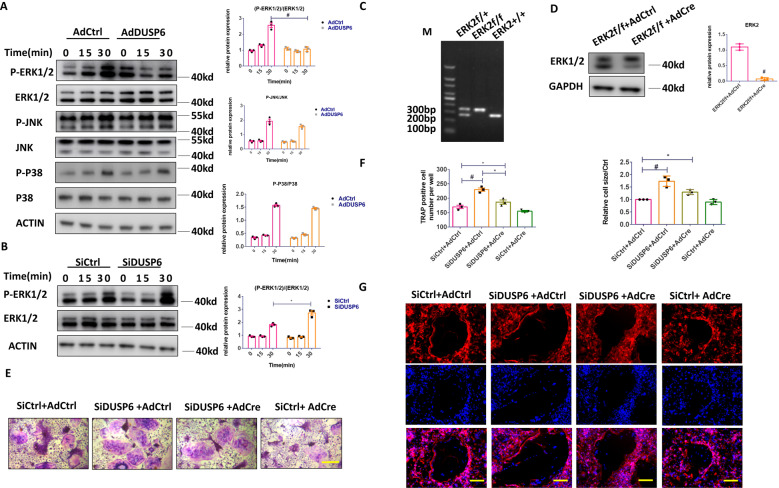
Fig. 7. DUSP6 regulated the osteoclastogenesis via ERK2 signaling.
RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation was established. A BMMs were transfected with Ad-Control (AdCtrl) and Ad-DUSP6. And phosphorylation of ERK1/2, P38, and JNK signaling pathway was analyzed for the indicated time point. B BMMs were transfected with SiControl(SiCtrl) and SiDUSP6. And the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was examined. C The genotyping analysis was carried out using PCR to confirm the ERK2 deletion according to the following standard: ERK2 wt: only 275 bp; ERK2f/+: 275 bp + 350 bp; ERK2f/f: only 350 bp. D BMMs were isolated from the ERK2f/f mice. And then they were transfected with Adcontrol(AdCtrl) and AdCre to delete the EKR2 expression. Western blot analysis was carried out to confirm this result. E BMMs isolated from the ERK2f/f mice were transfected to SiCtrl, SiDUSP6, AdCtrl, and AdCre in the indicated group. TRAP staining was carried out to explore the osteoclast differentiation. F Quantitative analysis was carried out. Original scale bars: 200 μm. G F-actin ring formation was carried out to explore the function of mature osteoclast. Original scale bars: 200 μm. Data in all bar graphs are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05, #P < 0.01.