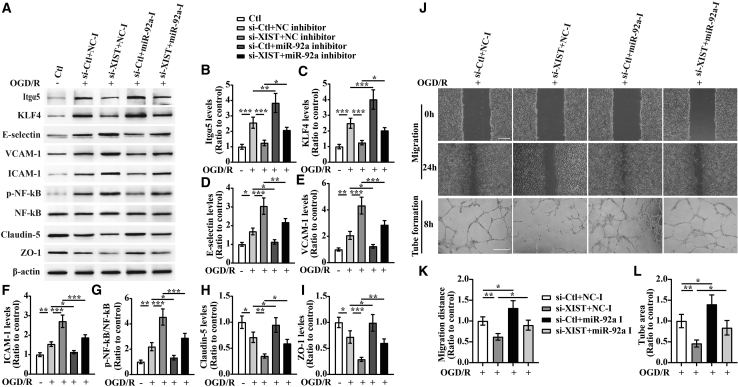
Figure 6.
lncRNA XIST alleviates a vascular endothelial inflammation response and regulates migration and tube formation of bEnd3 cells under OGD/R conditions by targeting miR-92a
(A) Representative images of western blot for the expression of Itgα5, KLF4, E-selectin, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, p-NF-κB, Claudin-5, and ZO-1 in bEnd3 cells co-transfected with the si-Ctl or si-XIST and/or miR-92a inhibitor (miR-92a-I) at 24 h restoration from OGD. (B−I) Bar graphs show the quantitative analyses of western blots as ratios of Itgα5/β-actin (B), KLF4/β-actin (C), E-selectin/β-actin (D), VCAM-1/β-actin (E), ICAM-1/β-actin (F), p-NF-κB/total NF-κB (G), Claudin-5/β-actin (H), and ZO-1/β-actin (I) (n = 4 per experimental group). Note that the expressions of Itgα5, KLF4, and TJPs (Claudin-5 and ZO-1) in the si-XIST + NC inhibitor (NC-I)-treated bEnd3 cells markedly decreased, but the expressions of three CAMs including E-selectin, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1 and the p-NF-κB were significantly elevated relative to the si-Ctl + NC-I-treated group at 24 h restoration from OGD. However, these effects were significantly rescued by inhibiting the levels of miR-92a in the bEnd3 cells. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. (J) Representative images of cell migration and capillary tube formation of bEnd3 cells transfected with si-Ctl or si-XIST and/or miR-92a-I after OGD/R treatment. Scale bar, 400 μm for migration; 500 μm for tube formation. (K and L) Quantification of cell migration (K) and tube formation (L) of bEnd3 cells (n = 4 per experimental group). Note that inhibition of miR-92a led to an increased migration and capillary-like tube formation of bEnd3 cells under OGD/R conditions, and miR-92a inhibition could reverse the inhibitory effects of XIST silencing on migration and tube formation of bEnd3 cells after OGD/R. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01.