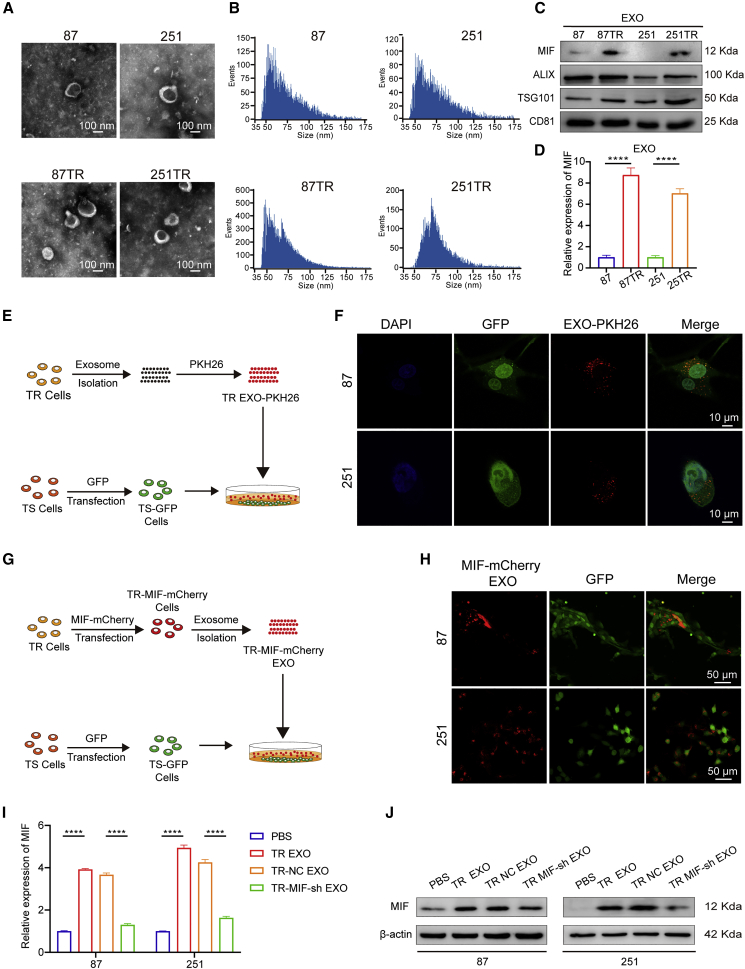
Figure 3.
Exosomal MIF transfers from TR cells to TMZ-sensitive cells
(A) The representative micrograph of round-shaped vesicles derived from TMZ-resistant and TMZ-sensitive cells by TEM (scale bars, 100 nm). (B) The nFCM further identified that the similar predominant size of these vesicles. (C) Western blot analysis showed the presence of MIF, ALIX, TSG101, and CD81 in exosomes. (D) qRT-PCR showed that the exosomes secreted by TR cells (TR EXO) expressed more MIF than those from TS cells. (E and F) Schematic diagram: TR exosomes were labeled with PKH26 and co-incubated with TS-GFP cells. Confocal photography found that exosomes could be successfully ingested by TS cells (scale bars, 10 μm). (G and H) Schematic diagram: MIF in TR cells was labeled with mCherry, and then exosomes were extracted and added into the supernatant of TS-GFP cells. After 24 h of coculture, we observed strong red fluorescence in the cytoplasm of TS-GFP cells (scale bars, 50 μm). (I and J) qRT-PCR and western blot were used to verify the expression level of MIF in TS cells after they were co-incubated with PBS, TR EXO, TR-NC EXO, or TR-MIF-sh EXO separately. ∗∗∗∗p<0.0001.