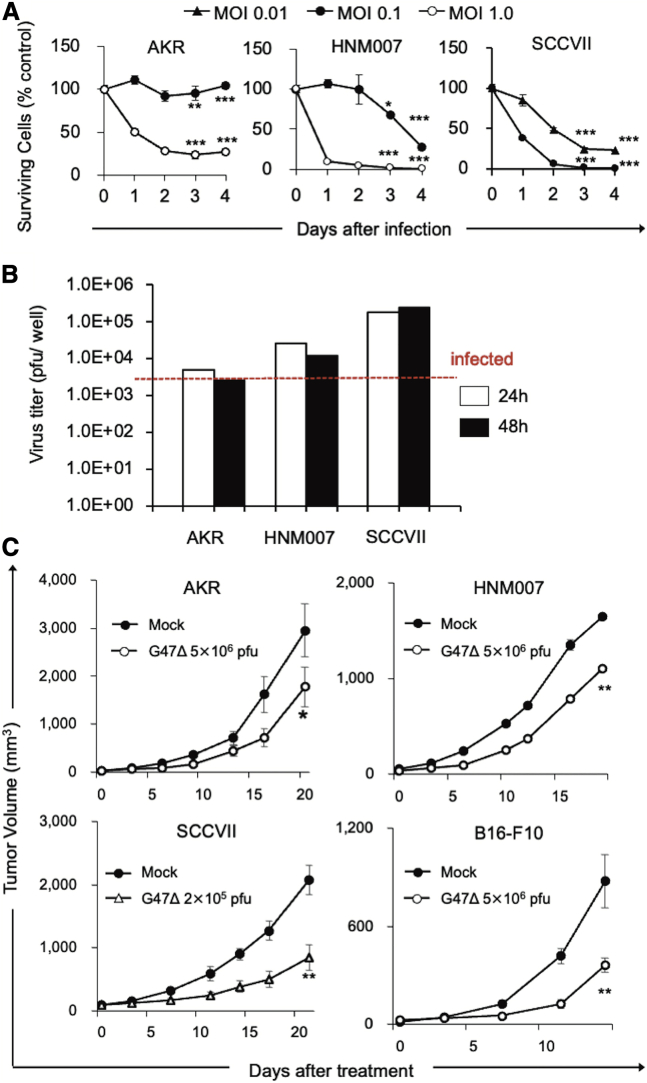
Figure 1.
In vitro and in vivo effects of G47Δ in murine carcinomas
(A) Cytopathic effects of G47Δ in vitro. Murine cancer cells were infected with G47Δ (AKR, HNM007, MOI of 0.1 [●] or 1 [○]; SCCVII, MOI of 0.01 [▲] or 0.1 [●]) or mock. Cell viability was expressed as a percentage of the mock-infected controls. G47Δ exhibited a good cytopathic effect in AKR and HNM007 cell lines at an MOI of 1.0 and in SCCVII at an MOI of 0.1. Data are presented as the mean of triplicates ± SD. (B) Virus yields of G47Δ in vitro. Murine cancer cells were infected with G47Δ at an MOI of 0.1, and recovered virus yields were determined at 24 and 48 h after infection. All murine cancer cell lines tested supported the replication of G47Δ to a certain extent. The results are presented as the mean of triplicates ± SD. (C) Four syngeneic murine subcutaneous tumor models (AKR [upper left], HNM007 [upper right], SCCVII [lower left], and B16-F10 [lower right]) were used. Established tumors, 5–6 mm in diameter, were inoculated with G47Δ (2 × 105 for SCCVII and 5 × 106 PFUs for others) or mock on days 0 and 3. The G47Δ treatment significantly inhibited the growth of subcutaneous tumors compared with the mock treatment in all models. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 7). One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was used to determine statistical significance (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001).