Figure 1.
Variable effects of Kir2.1eGFP-mediated neuronal silencing using multiple established DN1p GAL4 drivers
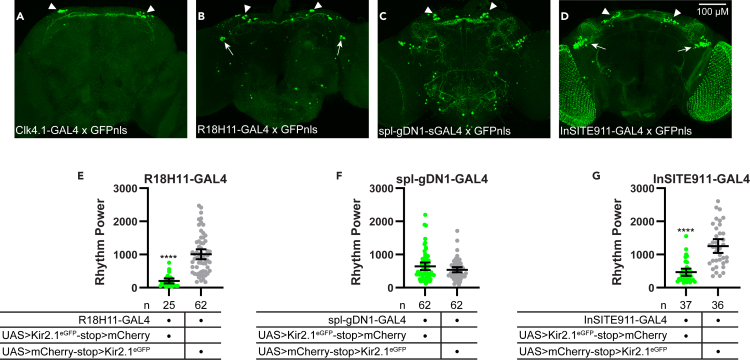
(A–D) Representative maximum-projection confocal images of brains in which GAL4 lines were used to drive expression of a nuclear-localized GFP (GFPnls). Brains were stained for GFP immunofluorescence (green). Arrowheads indicate GFP+ DN1 cells. Arrows in (B) indicate GFP+ LNd clock cells in the R18H11-GAL4 line. Arrows in (D) indicate GFP+ non-clock cells in the vicinity of the LNds in the InSITE911-GAL4 line.
(E–H) Rest:activity rhythm power over 6 days in DD is displayed for the genotypes listed. Lines are means ±95% confidence intervals. Dots represent individual flies. Experimental lines (GAL4 x UAS>Kir2.1eGFP-stop>mCherry) are in green, and control lines (GAL4 x UAS>mCherry-stop>Kir2.1eGFP) are in gray. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, t test. ns listed are number of flies that survived throughout the behavioral monitoring.