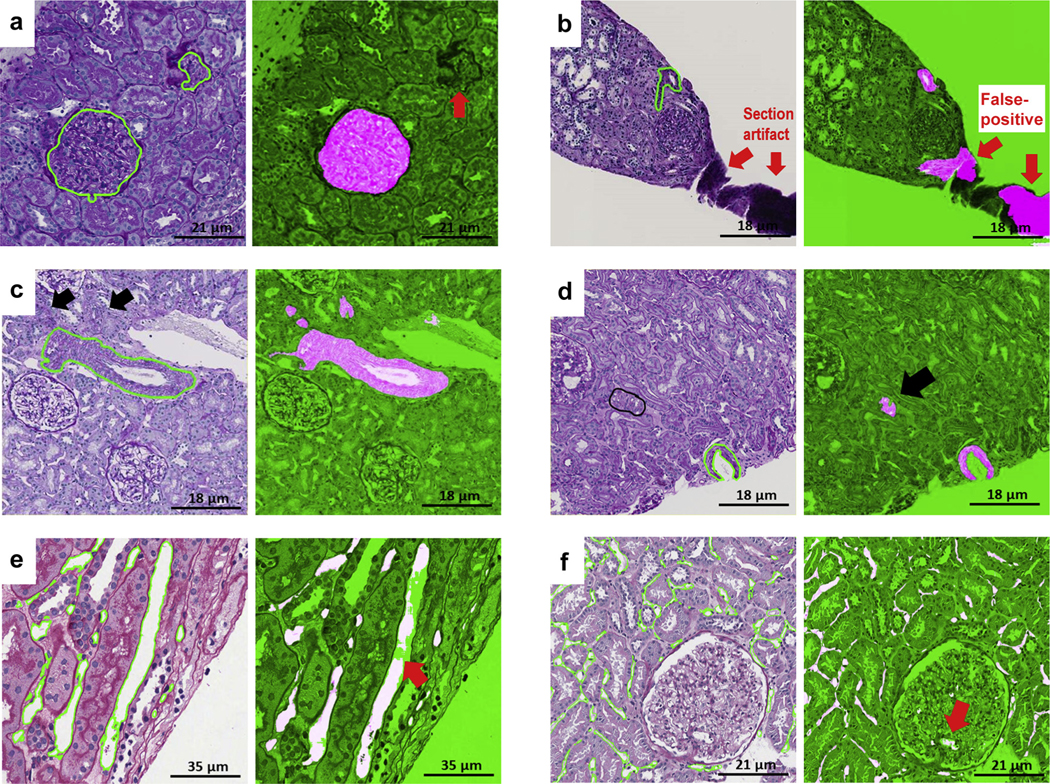
Figure 9|. Examples of false positive and false negative deep learning (DL) segmentations on periodic acid–Schiff (PAS).
(a) Glomerular unit: DL failed to detect a tangentially cut glomerular unit that does not have a typical round shape (red thick arrow). (b) Artery: section artifact generate a false positive (red thick arrows). (c) Arteries: black arrows show 2 arterioles missed by the pathologist but detected by DL. (d) Arteries: pathologists were instructed to segment artery when lumen was present; however, DL segmentation detected tangentially cut artery (thick black arrow) where only the medium was visible. (e) Peritubular capillaries: a long peritubular capillary reveals only partial DL segmentation at the pixel level. (f) Peritubular capillaries: DL network for peritubular capillaries detects a few glomerular capillaries (false positive; thick red arrow).