Fig. 2.
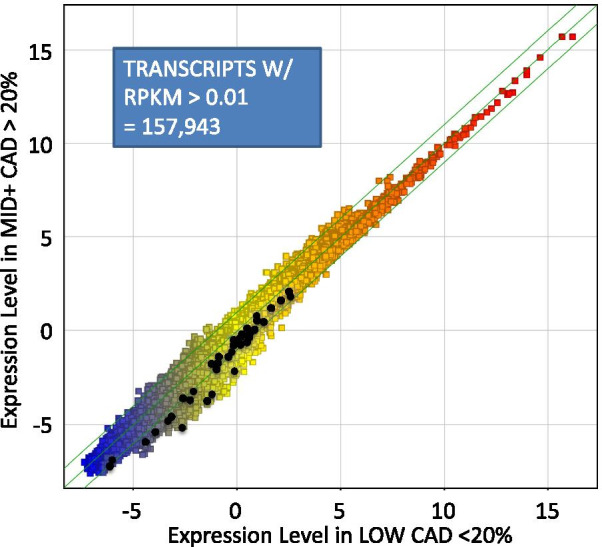
Genome-wide transcript profiling by RNAseq. A total of 96 patients with angiographic results were analyzed by RNAseq of whole blood RNA depleted of ribosomal sequences. The short reads were aligned to the human transcriptome (hg19) and counted per transcript. The raw read counts (R) were normalized only by (Per) the length of the transcript (K) and the total number of reads obtained per patient in millions (M) to yield RPKM. The RPKM is expressed on a log2 scale and averaged across all patients in the LOW CAD group (n = 48, X axis) versus patients in the MID+ CAD group (n = 48, Y axis). Each point represents one transcript where the RPKM was > 0.01 RPKM in 70% of samples in at least one group (157,943 transcripts). Black points represent a set of transcripts identified as differentially expressed between the 2 groups by a statistical analysis of fold-change and t-test probability (p < 0.001 uncorrected, and fold change > 1.5) resulting in 59 transcripts (49 unique, non-redundant)
