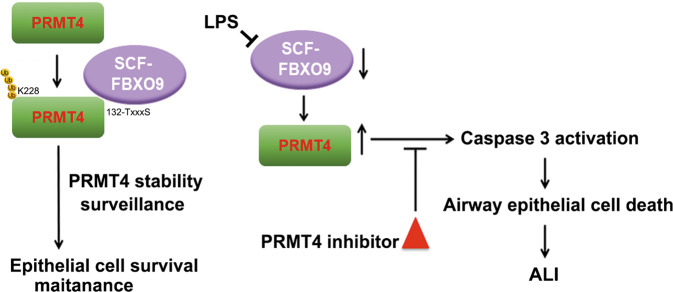
Fig. 8. Schematic presentation of the role of PRMT4 and SCFFBXO9 in airway cell death.
Left: PRMT4 is normally degraded via a SCFFBXO9 E3 ligase-mediated ubiquitin proteasomal pathway to maintain airway epithelial cell survival. SCFFBXO9 recognizes PRMT4 via a phosphodegron and poly-ubiquitinates PRMT4 at K228. Bacterial endotoxin reduces FBXO9 levels that results in PRMT4 protein accumulation. Increased PRMT4 activates caspase 3 to induce lung epithelial apoptosis during bacterial infection.