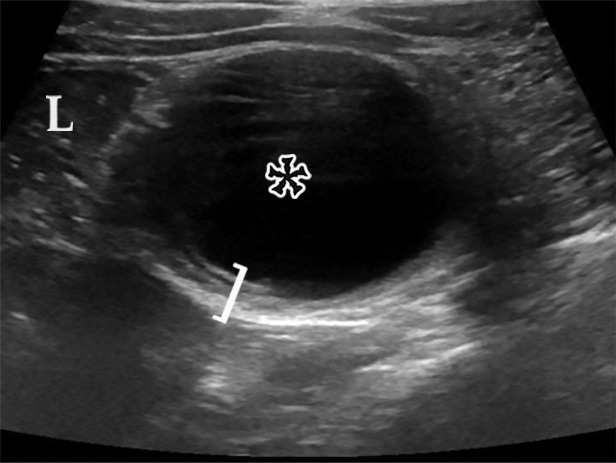
Figure 12a.
EDC with pathologic correlation. (a) Transabdominal US image at the level of the inferior margin of the liver (L) shows the gut signature sign (also known as the double-wall or five-layer sign) of the EDC wall. The multilayered alternating echogenic appearance resembles normal bowel, with similar innermost hyperechoic mucosa, hypoechoic muscularis mucosa, hyperechoic submucosa, hypoechoic muscularis propia, and outermost hyperechoic serosa (bracket) of the duplicated bowel wall of the EDC (*). This cyst served as the lead point for an intussusception (shown in Fig E5) and was resected. (b) Photograph of a cut gross specimen shows the common wall (arrowheads) of the EDC and subjacent bowel loop. Lumen = small-bowel lumen. (c) Low-power photomicrograph (H-E stain) of an EDC shows the shared wall (*) between the small-bowel loop and EDC. Arrowheads = mucosae.