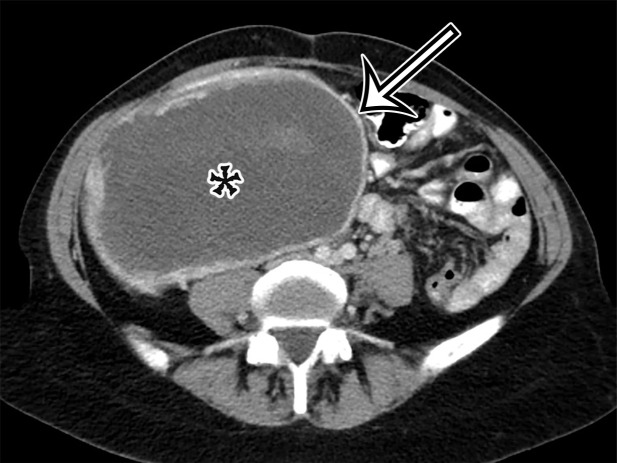
Figure 18a.
Spectrum of cystic gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) at axial contrast-enhanced CT. (a) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image in a 35-year-old woman with right-sided bulging of the abdomen shows a large unilocular thick-walled cyst in the right abdomen (arrow) with no obvious site of origin. The internal contents have heterogeneous attenuation (*). (b) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image in a 61-year-old man with new-onset abdominal pain similarly shows a large predominantly unilocular cystic mass (*) in the anterior abdomen, with a thick wall (arrow) and mass effect on the pancreas and stomach but no clear site of origin. (c) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image in a 50-year-old woman shows a solid and cystic mass in the anterior abdomen. The cystic components (*) are more loculated, with thick walls and large solid components (arrow), consistent with cystic degeneration of a high-risk GIST.