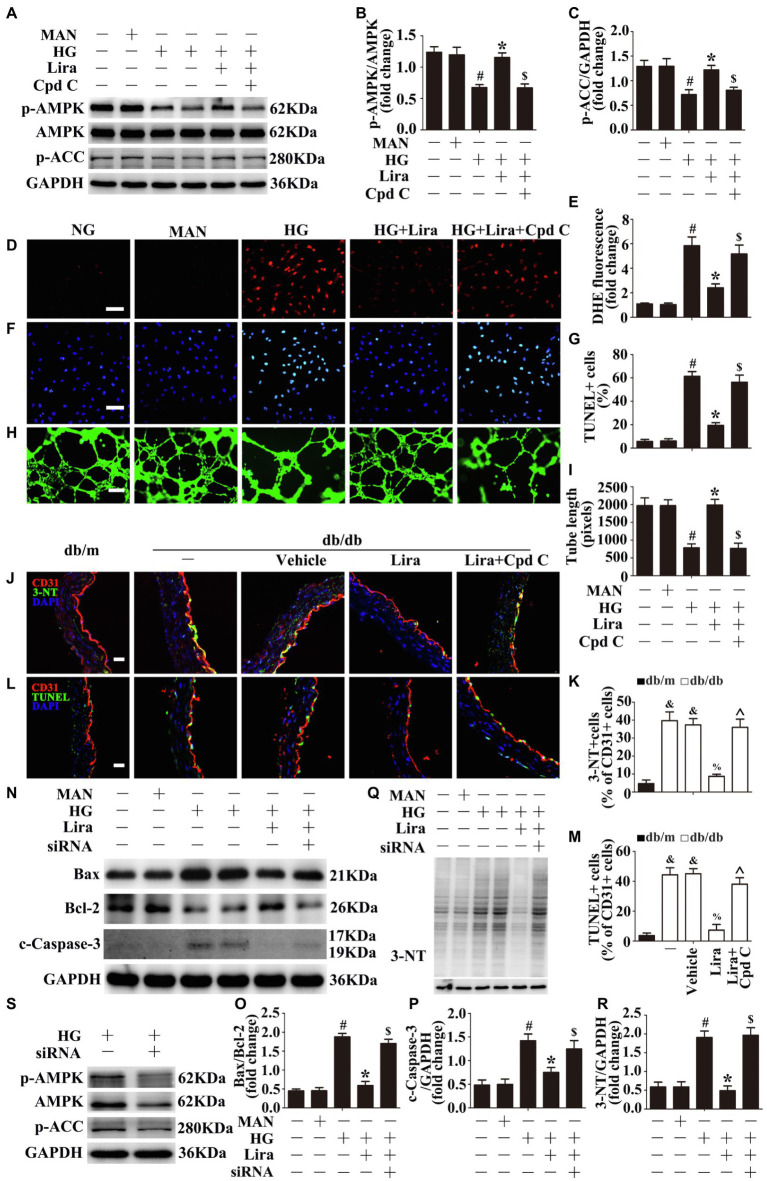
Figure 2.
The endothelial protective action of Lira against hyperglycemia is AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent. (A) Cell lysates of HUVECs were used to detect the p-AMPK and phosphorylated acetyl-CoA carboxylase (p-ACC) protein levels by immunoblotting. HUVECs were cultured either in NG or HG medium alone or with Lira (100 nM) for 72 h, MAN served as the osmotic control for the HG. For signaling pathway analysis, Compound C (Cpd C) inhibitor of AMPK (10 μM) was pretreated for 2 h before Lira administration. (B,C) The quantitative analysis of each immunoblot. (D) Fluorescence with DHE, scale bars = 100 mm, (F) TUNEL assay, scale bars = 100 mm, and (H) capillary-like tube formation, scale bars = 300 mm. HUVECs were treated as indicated in (A). (E) Quantification of the DHE fluorescence intensity ratio, (G) the quantitative analysis of TUNEL+ cells, and (I) the tube length. (J) The representative images of immunofluorescence with 3-NT, scale bars = 20 μm and (L) endothelial cells TUNEL assay, scale bars = 20 μm, from db/m mice, db/db mice, and db/db mice receiving Lira (200 μg/kg/day) or vehicle treatment with saline infusion aorta tissue sections. For signaling pathway analysis, Cpd C inhibitor of AMPK, was administered at the dose of 1.5 mg/kg/day. (K) Quantification of the proportion of 3-NT positive cells and (M) TUNEL-positive cells of CD31+ cells. (N,Q,S) Cell lysates of HUVECs were used to detect the Bax, Bcl-2, c-Caspase-3, 3-NT, p-AMPK, and p-ACC protein levels by immunoblotting. HUVECs were transfected with si-AMPKα1/α2 or control siRNA, respectively. After transduction, HUVECs were cultured either in NG, or HG medium alone or with Lira (100 nM) for 72 h. (O,P,R) The quantitative analysis of each immunoblot. All values displayed are means ± SEM of five independent experiments. &p < 0.05 vs. db/m mice; %p < 0.05 vs. db/db mice or vehicle-treated db/db mice; ^p < 0.05 vs. db/db mice receiving Lira; #p < 0.05 vs. NG or MAN; *p < 0.05 vs. HG; $p < 0.05 vs. HG co-incubated with Lira.