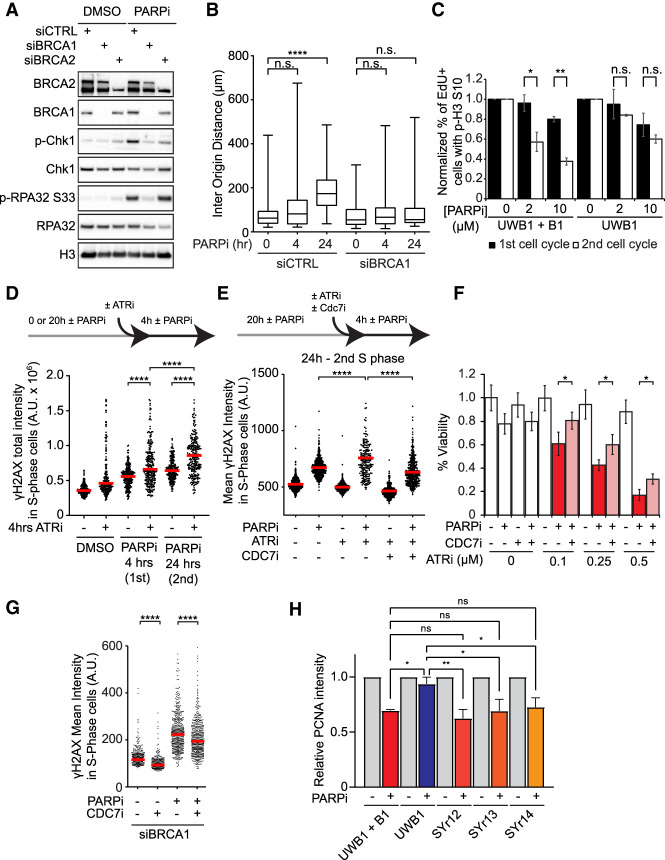
Figure 6.
Levels of origin firing and overall DNA synthesis are determinants of PARPi sensitivity. (A) BRCA1/2-deficient cells are defective for ATR activation in the second S phase. Cells were treated with DMSO or 10 µM olaparib for 24 h. Levels of the indicated proteins were analyzed by western blot. (B) BRCA1-deficient cells are unable to suppress origin firing in the second S phase. Cells were treated with 10 µM olaparib for the indicated durations and analyzed by CldU/IdU labeling (20 min each) and DNA combing. More than 320 CldU/IdU double-positive replication tracts were analyzed for inter-origin distance in each sample (n > 320). Significance was determined with a two-tailed Student's t-test. (****) P-value < 0.0001, (n.s.) P-value > 0.05. (C) BRCA1-deficient UWB1 cells fail to activate the G2/M checkpoint in the second S phase. UWB1 and UWB1+B1 cells were analyzed as in Figure 1C. Error bars indicate SD of two independent experiments. Significance was calculated with a two-tailed Student's t-test. (*) P-value < 0.05, (**) P-value < 0.01, (n.s.) P-value > 0.05. (D) ATR is critical for suppressing DNA damage in the second S phase. U2OS cells were treated with 10 µM olaparib for the indicated durations. VE-821 (ATRi; 10 µM) was added during the last 4 h as indicated, and S-phase cells were labeled with 10 µM EdU during the last 15 min. The total intensity of γH2AX foci in S-phase cells was quantified. (Red bar) Median intensity. More than 200 S-phase cells were analyzed in each sample (n > 200). Significance was determined with a Mann–Whitney U test. (****) P-value < 0.0001. (E) Inhibition of origin firing suppresses the induction of DNA damage by ATRi in the second S phase. U2OS cells were treated with DMSO or 10 µM olaparib for 24 h. VE-821 (ATRi; 10 µM) and/or XL-413 (CDC7i; 5 µM) were added during the last 4 h, and S-phase cells were labeled with 10 µM EdU during the last 15 min. The mean intensity of γH2AX in S-phase cells was quantified. (Red bar) Median intensity. More than 200 S-phase cells were analyzed in each sample (n > 200). Significance was determined with a Mann–Whitney U test. (****) P-value < 0.0001. (F) ATRi enhances PARPi sensitivity by increasing origin firing. U2OS cells were treated with increasing concentrations of VE-821 (ATRi), 1 µM olaparib (PARPi), and 1 µM XL-413 (CDC7i) as indicated for 6 d. Cell viability was determined with CellTiter Glo. Three technical replicates were analyzed in each sample (n = 3). Significance was determined with a two-tailed Student's t-test. Error bar indicates standard deviation. (*) P-value < 0.01. (G) Inhibition of origin firing suppresses PARPi-induced DNA damage in BRCA1-deficient cells. U2OS cells were transfected with BRCA1 siRNA for 48 h and then treated with DMSO or 10 µM olaparib for 24 h in the presence or absence of 1 µM XL-413. S-phase cells were labeled with EdU during the last 15 min. The mean γH2AX intensity in S-phase cells was quantified. (Red bar) Median intensity. More than 200 S-phase cells were analyzed in each sample (n > 200). Significance was determined with a Mann–Whitney U test. (****) P-value < 0.0001. (H) The ability to suppress overall DNA synthesis in the second S phase correlates with PARPi resistance in cancer cell lines. The indicated cell lines were treated with DMSO or 10 µM olaparib for 24 h, and S-phase cells were labeled with 10 µM EdU in the last 15 min. PCNA levels in EdU+ cells were then quantified by immunofluorescence and normalized to the untreated DMSO control of each cell line. At least 200 cells were analyzed in each condition (n ≥ 200). Error bars indicate SD of three independent experiments. Significance was calculated with a one-way ANOVA with the Tukey procedure. (*) P-value < 0.05, (**) P-value < 0.01, (n.s.) P-value > 0.05.