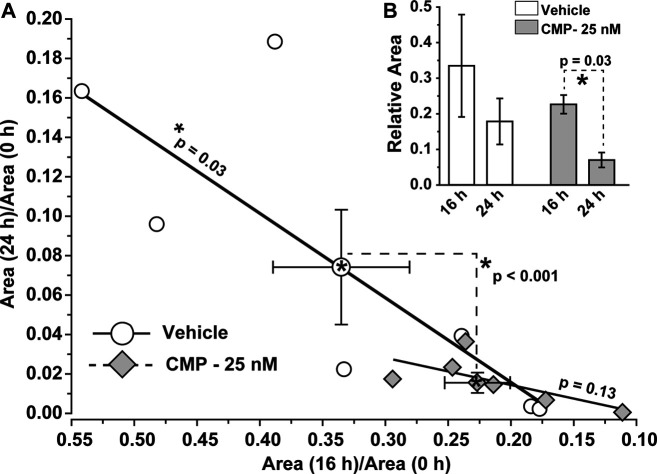
FIGURE 3.
CMP accelerates the rate of epithelium wound closure. (A) For vehicle-treated eyes, the ratio of residual wound area at 24 h to initial (0 h) size decreases with a diminishing ratio of the area at 16 h to initial. The slope of the best-fitting regression line differs significantly from 0 (*, p = 0.03). For CMP-treated eyes (25 nM), accelerated closure clusters both ratios at smaller values, yielding an insignificant regression (p = 0.13). The cluster of ratios for a vehicle vs. CMP cohorts differed significantly (dashed lines, p < 0.001), as shown by multivariable analysis of variance to compare the means (mean ± SEM) (B, inset). Relative wound size calculated as the ratio of residual wound area at 16 h to initial and at 24 compared to 16 h for vehicle- and CMP-treated eyes (mean ± SEM). Wound area diminished significantly between 24 and 16 h compared to the initial 16 h period for CMP eyes (p = 0.03) but not for a vehicle (p = 0.10). Importantly, initial wound size for CMP-treated eyes (1.41 ± 0.13 mm) did not differ from vehicle-treated eyes (1.54 ± 0.17 mm, p = 0.38; n = 7 for each cohort).