FIGURE 2.
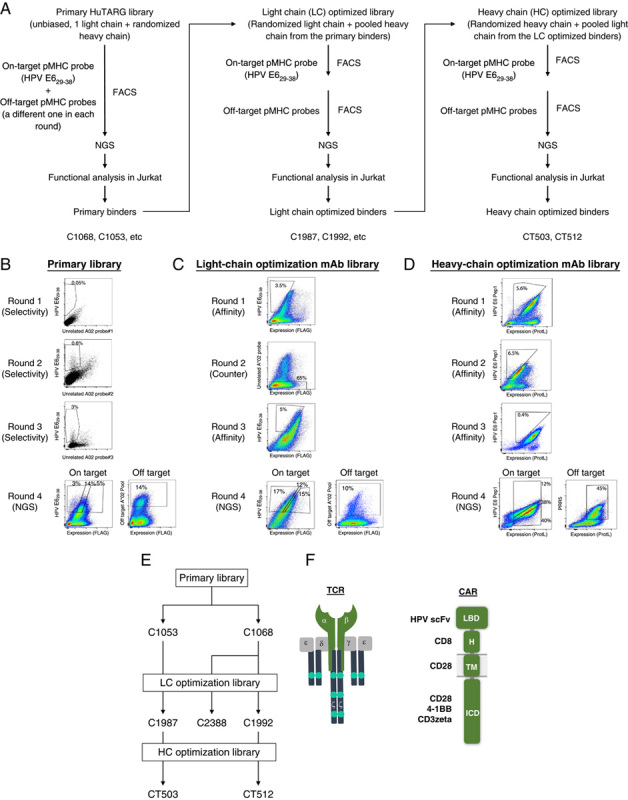
Overview of sorting strategy and representative scatter plots. HPV E629–38 is used as an example. A, Flowchart of the HuTARG library, FACS, and optimization process. B, An unbiased HuTARG library was screened against HPV E629–38 pMHC mixed with an unrelated pMHC probe to serve as counterscreen in each round. Cells that bound to HPV E629–38 pMHC were enriched over 3 rounds of FACS, while nonspecific binders were depleted by gating against cells binding the counterscreen probe. Subsequently, cells with high, medium, and low on-target probe binding and off-target probes binding were collected separately. cDNAs were generated from these cells and pooled with barcodes. Complementarity-determining regions of binders were determined by NGS using pooled cDNA samples. C, Thirty-two HPV E629–38 binders from the primary HuTARG library (primary binders) were selected based on their functional activity in Jurkat assays as parents for light-chain optimization. A HuTARG library was built containing a mixture of binders with light-chain variations paired with the heavy chains from the 32 parents. The optimization library was screened against HPV E629–38 using the same strategy as the primary library, except that the on-target and off-target counterscreen were done in separate rounds by fluorescence-activated cell sorter. D, Thirty-five binders from the light-chain optimization library were selected based on their functional activity in Jurkat assays as parents for heavy-chain optimization. A HuTARG library was built containing a mixture of binders with heavy-chain variations paired with the light chains from the 35 parents. The optimization library was screened against HPV E629–38 using the same strategy as the light-chain optimization library. E, Diagram of relationships of the HPV E6 binders tested. F, Structural diagram of CARs and TCRs tested. CAR indicates chimeric antigen receptor; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorter; HPV, human papillomavirus; ICD, intracellular domain; LBD, ligand-binding domain; mAb, monoclonal antibody; NGS, next-generation sequencing; pMHC, peptide-loaded major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T-cell receptor.
