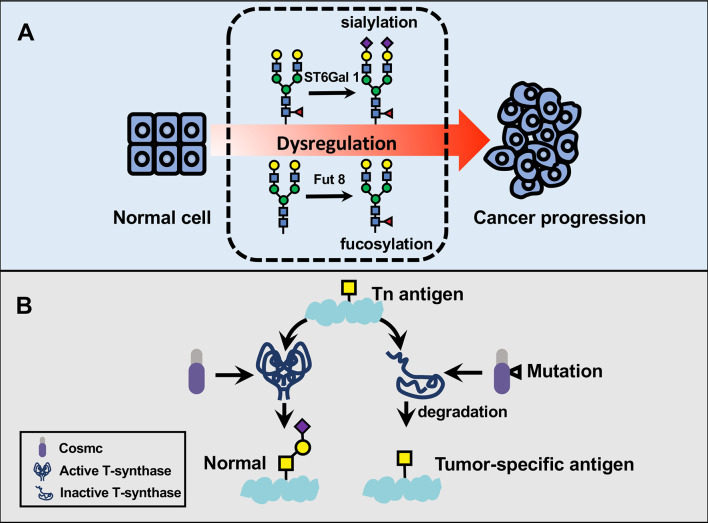
Figure 2.
The participation of dysregulated glycosylation in cervical cancer progression. (A) Glycans play fundamental parts in key pathological steps of tumor development and progression. α2,6-sialyltransferase I (ST6Gal 1) and α2,6-linked sialylation play fundamental parts in pathological steps of cancer progression. ST6Gal 1 attaches an α2,6-linked sialic acid to Galβ1,4GlcNAc usually via an α2,6 linkage, thereby serving as a regulator in cervical cancer metastasis. Cervical cancer tissues also exhibit aberrant fucosylation in the cytosolic proteins compared to normal tissues. (B) Tn antigen is a major driving carbohydrate antigen in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Cosmic is mostly known as an essential chaperone required for T-synthase activity, which can convert Tn antigen to a common precursor T antigen for further extension in the Golgi apparatus. In contrast, the somatic mutation in cosmic has been associated with a loss of T-synthase and subsequent accumulation of Tn antigen in cervical cancer specimen.