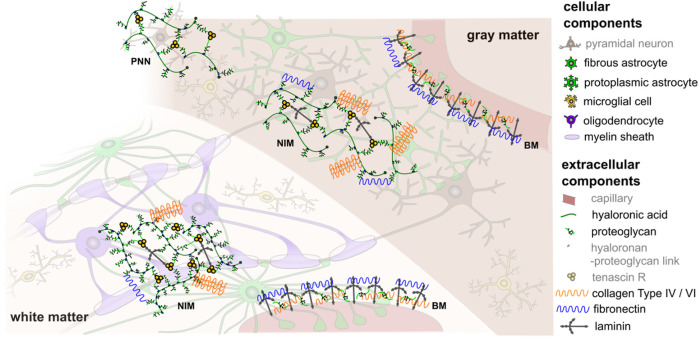
FIGURE 2.
Schematic illustration of the cellular and extracellular components of human brain tissue (components greyed out are not further considered in the present work). White matter contains oligodendrocytes, which wrap myelin sheath around axons, as well as fibrous astrocytes and microglia. Gray matter contains mainly neurons, protoplasmic astrocytes, and microglia. The extracellular matrix has three principal compartments: the basement membrane (BM), which lines cerebral microvessels and the pial surface, the neural interstitial matrix (NIM), which is diffusely distributed in the brain’s interstitial space, and perineuronal nets (PNN), which surround inhibitory interneurons in certain areas of gray matter. In different compositions, these compartments contain proteoglycans, hyaluronic acid, link proteins, glycoproteins (e.g., tenascin, laminin, fibronectin), and non-fibrillar collagens type IV and VI (Lau et al., 2013). This is a schematic figure for identification purposes only with no claim of being complete or true to scale. Reprinted from Budday et al. (2020b) with permission from Elsevier.