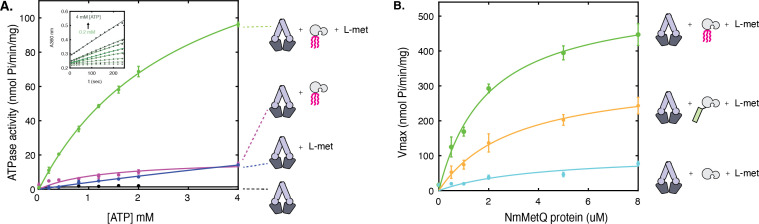
Figure 2. ATP hydrolysis of NmMetNI in the presence and absence of L-methionine and NmMetQ proteins.
(A) ATP hydrolysis was measured in the presence of 1 μM of DDM-solubilized NmMetNI alone (black trace), 50 μM L-methionine (blue trace), 1 μM lipo-NmMetQ (magenta trace) and both 50 μM L-methionine and 1 μM lipo-NmMetQ (green trace). Insert shows representative measurements of absorbance versus time (black dots) and the linear fits (green lines) for NmMetNI ATPase activity in the presence of lipo-NmMetQ and L-methionine at increasing ATP concentrations (0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2.0, and 4.0 mM) (B) Specific activity of NmMetNI with increasing concentrations of various NmMetQ proteins: lipo-NmMetQ (green trace), pre-protein NmMetQ (orange trace), and secreted NmMetQ (cyan trace) with 50 μM L-methionine. Vmax values were determined by fitting the Michaelis-Menten equation to a plot of ATPase activity versus ATP concentration (0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2.0, and 4.0 mM) at different MetQ protein concentrations ( 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 5, 8 μM). N=3 error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). These data show the NmMetNI ATPase activity is tightly coupled, requiring both L-methionine and lipo-NmMetQ for maximal NmMetNI ATPase stimulation.