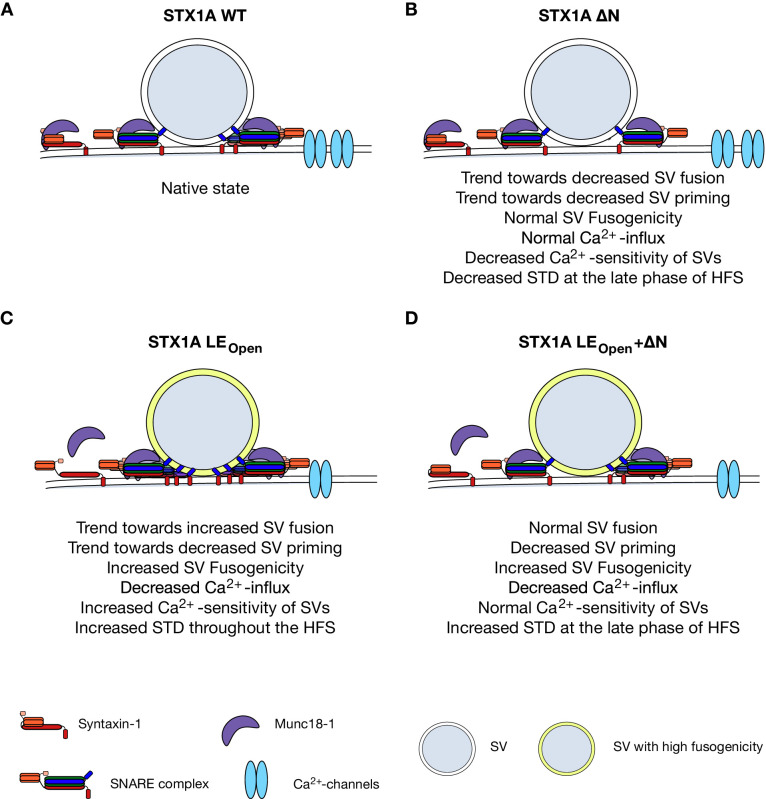
Figure 8. Speculative model of effects of N-peptide deletions and LEOpen mutation on vesicular release.
(A) Native state of STX1A. (B) N-peptide deletion of STX1A leads to a decrease in Ca2+-sensitivity of vesicular release and short-term depression (STD) upon 10 Hz stimulation potentially through increased distance of Ca2+-channel synaptic vesicle (SV) coupling. (C) LEOpen mutation on STX1A increases fusogenicity and Ca2+-sensitivity of SVs and thus leads to a high degree of STD. It also leads to reduced global Ca2+-influx. (D) SV fusion proceeds normal when LEOpen mutation is combined with N-peptide deletion. LEOpen mutation dictates SV fusogenicity and Ca2+-influx by increasing the former and decreasing the latter.